In Vitro Effect of Ferruginol, Tanshinone, and Carnosol Analogues on the Proliferation of Three Breast Cancer Cell Lines
- PMID: 40572493
- PMCID: PMC12195677
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30122529
In Vitro Effect of Ferruginol, Tanshinone, and Carnosol Analogues on the Proliferation of Three Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
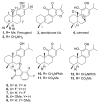
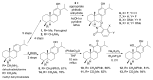
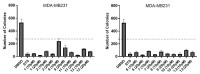
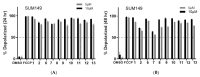
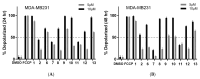
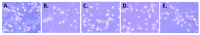
Ferruginol, tanshinones and carnosol are considered privileged natural products due to their demonstrated diverse biological activities with relevance to cancer research. Globally, cancer continues to be a major contributor to mortality rates, making these compounds potentially valuable molecular scaffolds for further development as potential anticancer agents. In this work, a focused library of ferruginol, tanshinone IIA, and carnosol analogues was studied to examine their effectiveness against various solid tumor models. The compounds were efficiently synthesized from either methyl 12-hydroxy-dehydroabietate or 12-hydroxydehydroabietylamine in 1-3 step processes with good chemical yields. The compounds that were synthesized underwent a methodical evaluation using multiple biological tests (including viability assays, clonogenic assays, and mitochondrial membrane polarization measurements) to determine their ability to inhibit in vitro the growth of three breast cancer cell linages. It was determined that while most compounds exhibited biological activity, compounds 10 and 11 demonstrated significant efficacy against triple negative breast cancer cells. These compounds continue to show promising biological activity, suggesting that additional studies to understand their mechanisms of action would be valuable.
Keywords: abietane; breast cancer cells; carnosol; cytotoxicity; ferruginol; tanshinone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
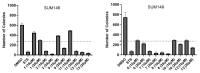
References
-
- Galukande M., Dos-Santos-Silva I., Ferlay J., Bray F., Ginsburg O., Vaccarella S., Soerjomataram I., Canfell K., Anderson B.O., Parham G., et al. Global and regional estimates of orphans attributed to maternal cancer mortality in 2020. Nat. Med. 2022;28:2563–2572. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-02109-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

