Visible-Light-Driven Co3O4/Nb2O5 Heterojunction Nanocomposites for Efficient Photocatalytic and Antimicrobial Performance in Wastewater Treatment
- PMID: 40572526
- PMCID: PMC12196055
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30122561
Visible-Light-Driven Co3O4/Nb2O5 Heterojunction Nanocomposites for Efficient Photocatalytic and Antimicrobial Performance in Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
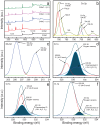
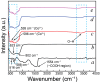
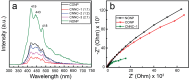
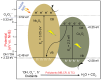
The development of high-performance photocatalysts is vital for combating water pollution and microbial contamination. In this study, visible-light-active Z-scheme heterojunction nanocomposites composed of Co3O4 and Nb2O5 (CNNC) were synthesized via co-crystallization and subsequent high-pressure annealing to enhance photocatalytic and antimicrobial performance. Structural and optical analyses via XRD, FESEM, TEM, XPS, and PL confirmed the heterojunction formation between porous Co3O4 nanoparticles (CONP) and columnar orthorhombic Nb2O5 nanoparticles (NONP). The CNNC exhibited significantly improved photocatalytic activity, achieving degradation efficiencies of 95.1% for methylene blue, 72.6% for tetracycline, and 90.0% for Congo red within 150 min. Kinetic studies showed that CNNC's rate constants were 367% and 466% of those of CONP and NONP, respectively. Moreover, CNNC demonstrated a strong antibacterial effect on Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli with ZOI values of 9.3 mm and 6.8 mm, respectively. Mechanistic analysis revealed that the Z-scheme charge-transfer pathway improved charge separation and reduced electron-hole recombination, contributing to the promoted photocatalytic efficiency. The nanocomposite also showed robust stability and recyclability over five times. These results highlight the promise of CNNC as a bifunctional, visible-light-driven photocatalyst for pollutant decomposition and microbial control.
Keywords: Co3O4/Nb2O5 visible-light-driven photocatalyst; antibacterial activities; heterojunction interface; synergistic effect; water pollutants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing interests in regard to the work reported in this paper.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Harnessing BiOI/V2O5 Nanocomposites: Advanced Bifunctional Catalysts for Visible-Light Driven Environmental Remediation and Antibacterial Activity.Molecules. 2025 Jun 6;30(12):2500. doi: 10.3390/molecules30122500. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40572466 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic photocatalytic and antimicrobial efficacy of poly(m-aminophenol)/reduced graphene oxide/cobalt oxide hybrid composite for organic dye degradation.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025 Jun;32(30):18156-18173. doi: 10.1007/s11356-025-36727-3. Epub 2025 Jul 11. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40646408
-
Investigation of Aloe vera mediated ZnO-β-CD nanocomposite for photocatalysis and antimicrobial applications.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22871. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05231-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595945 Free PMC article.
-
Bismuth-based heterojunction photocatalysts for antibiotic remediation: A review of tetracycline degradation and mechanistic insights.J Environ Manage. 2025 Aug 29;393:127010. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2025.127010. Online ahead of print. J Environ Manage. 2025. PMID: 40884951 Review.
-
Structural regulation and photocatalytic antibacterial performance of TiO2, carbon dots and their nanocomposites: a review.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2025 Dec 15;700(Pt 2):138482. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2025.138482. Epub 2025 Jul 23. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2025. PMID: 40716222 Review.
References
-
- Liu H., Ma S., Shao L., Liu H., Gao Q., Li B., Fu H., Fu S., Ye H., Zhao F., et al. Defective engineering in graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet for efficient photocatalytic pathogenic bacteria disinfection. Appl. Catal. B. 2020;261:118201. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118201. - DOI
-
- Karim M.N., Singh M., Weerathunge P., Bian P., Zheng R., Dekiwadia C., Ahmed T., Walia S., Della Gaspera E., Singh S., et al. Visible-light-triggered reactive-oxygen-species-mediated antibacterial activity of peroxidase-mimic CuO nanorods. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018;1:1694–1704. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.8b00153. - DOI
-
- Makvandi P., Wang C.y., Zare E.N., Borzacchiello A., Niu L.n., Tay F.R. Metal-based nanomaterials in biomedical applications: Antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity Aspects. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020;30:1910021. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201910021. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

