Accurate Prediction of Drug Activity by Computational Methods: Importance of Thermal Capacity
- PMID: 40572530
- PMCID: PMC12196145
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30122563
Accurate Prediction of Drug Activity by Computational Methods: Importance of Thermal Capacity
Abstract
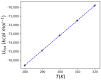
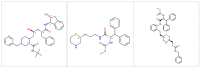
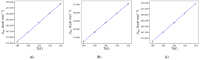
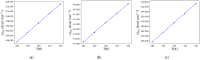
Heat capacity is one of the most important thermodynamic quantities in protein biochemistry. Upon the binding of small molecules, a change in the heat capacity of proteins is generally observed, and this is often used in drug discovery. However, few computational works dedicated to the study of these phenomena are available in the literature. Here, a simple computational method for determining the change in heat capacity upon the binding of small ligands has been evaluated. The method is based on the accurate calibration of the solvent's thermal properties in the simulation conditions used in order to simply subtract its contribution to calculate the variations in the heat capacity of the system of interest. Using HIV protease as a model system, for which numerous experimental thermodynamic data are available, estimates of the change in heat capacity upon binding were obtained, which were similar to those observed experimentally. Furthermore, the predicted variations in heat capacity appear to be able to discriminate between molecules that behave as effective inhibitors of the enzyme and molecules that are able to bind the enzyme but not inhibit it. The results obtained suggest that this computational approach could be a useful aid in the in silico screening of new ligands for targets of interest.
Keywords: HIV; heath capacity; ligands; molecular dynamics simulation; protease; protein binding; thermodynamics; water.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapy for Gaucher's disease: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Jul;10(24):iii-iv, ix-136. doi: 10.3310/hta10240. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16796930
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

