Influence of Ionic Strength and Temperature on the Adsorption of Reactive Black 5 Dye by Activated Carbon: Kinetics, Mechanisms and Thermodynamics
- PMID: 40572556
- PMCID: PMC12195980
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30122593
Influence of Ionic Strength and Temperature on the Adsorption of Reactive Black 5 Dye by Activated Carbon: Kinetics, Mechanisms and Thermodynamics
Abstract
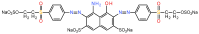
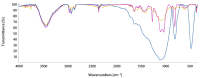
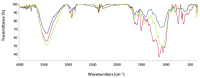
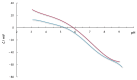
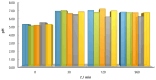
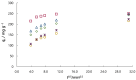
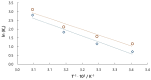
The aim of this work was to investigate the influence of ionic strength and temperature on the adsorption of Reactive Black 5 dye on commercial powdered activated carbon. Adsorption experiments were performed at 45 °C with the addition of NaCl (c0 = 0.01, 0.05, 0.10 and 1.00 M) and Na2SO4 (c0 = 0.01 M). The results were compared with those obtained for both salts (c0 = 0.01 M) at three additional temperatures: 25, 35 and 55 °C. For all adsorption experiments, kinetic and thermodynamic studies were performed. This research showed that the addition of NaCl, even in the concentration of only c0 = 0.01 M, significantly enhanced dye adsorption and that higher NaCl concentration resulted in higher adsorption capacity. In addition, slightly higher adsorption was observed when Na2SO4 was added to the dye solution at the same concentration as NaCl, as well as at a higher temperature, regardless of the salt added to the dye solution. It was also shown that adsorption is kinetically controlled, assuming a pseudo-second-order model, and that intraparticle diffusion is not the only process that influences the adsorption rate. Finally, calculated thermodynamic parameter values for both salts (c0 = 0.01 M) indicate that adsorption was a spontaneous endothermic process.
Keywords: Reactive Black 5; activated carbon; ionic strength; isothermal adsorption; kinetics; thermodynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
References
-
- Yaseen D.A., Scholz M. Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: A critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019;16:1193–1226. doi: 10.1007/s13762-018-2130-z. - DOI
-
- Lellis B., Fávaro-Polonio C., Pamphile J., Polonio J. Effects of textile dyes on health and the environment and bioremediation potential of living organisms. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2019;3:275–290. doi: 10.1016/j.biori.2019.09.001. - DOI
-
- Singha K., Pandit P., Maity S., Sharma S.R. Harmful environmental effects for textile chemical dyeing practice. In: Ibrahim N., Hussain C.M., editors. Green Chemistry for Sustainable Textiles. Woodhead; Cambridge, UK: 2021. pp. 153–164.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

