Mediterranean Basin Erica Species: Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Properties
- PMID: 40572579
- PMCID: PMC12195928
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30122616
Mediterranean Basin Erica Species: Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Properties
Abstract
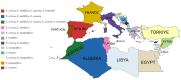
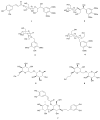
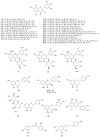
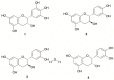
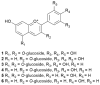
Erica species native to the Mediterranean basin are the principal Ericas that have found use in traditional medicine. Examples include treatments for urinary tract disorders, inflammatory conditions, gastrointestinal ailments and weight loss. This review critically evaluates the ethnobotanical usage, phytochemical profiles and pharmacological potential of the Mediterranean Erica species, including Erica arborea L., Erica multiflora L. and Erica manipuliflora Salisb. A wide spectrum of bioactive secondary metabolites has been identified across these species, notably pentacyclic triterpenes (e.g., lupeol, ursolic acid and oleanolic acid) and polyphenolics (e.g., myricetin and quercetin glycosides). Extracts of these species have demonstrated antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antimicrobial and diuretic activities in vitro and/or in vivo, providing pharmacological support for traditional uses. Phytochemical profiles vary by species, plant part, geography and extraction technique. Filsuvez®, comprising pentacyclic triterpenes from birch bark, has clinical approval for the treatment of partial thickness wounds associated with dystrophic and junctional epidermolysis bullosa. The undoubted reservoir of pentacyclic triterpenes and flavonoid glycosides in Mediterranean Erica species warrants further comprehensive mechanistic studies, toxicological evaluations and clinical validation.
Keywords: analgesics; anthocyanidins; anti-inflammatory; anti-microbials; anti-urolithiatics; diuretics; essential oils; mediterranean Ericas; polyphenolics; triterpenoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Christenhusz M.J., Byng J.W. The number of known plants species in the world and its annual increase. Phytotaxa. 2016;261:201–217. doi: 10.11646/phytotaxa.261.3.1. - DOI
-
- Fatima B., Anteur Djame L., Mohammed B. The study groups to Erica arborea phytoecologique in the north–west Algerian: Case of the forest bissa. Plant Arch. 2017;17:1478–1482.
-
- Kron K.A., Chase M.W. Systematics of the Ericaceae, Empetraceae, Epacridaceae and related taxa based upon rbcL sequence data. Ann. Mol. Bot. Gard. 1993;80:735–741. doi: 10.2307/2399857. - DOI
-
- McGuire A.F., Kron K.A. Phylogenetic relationships of European and African ericas. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2005;166:311–318. doi: 10.1086/427478. - DOI
-
- Ojeda F. Biogeography of seeder and resprouter Erica species in the Cape Floristic Region—Where are the resprouters? Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1998;63:331–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8312.1998.tb01521.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

