Topical Application of RNAi Therapy Using Surface-Modified Liposomes for Treating Retinal-Vein Occlusion
- PMID: 40572585
- PMCID: PMC12196029
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30122622
Topical Application of RNAi Therapy Using Surface-Modified Liposomes for Treating Retinal-Vein Occlusion
Abstract
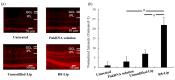
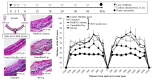
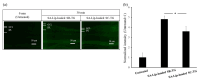
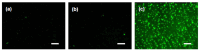
Retinal diseases can result in blindness and visual impairment. They represent a significant medical burden and adversely affect life expectancy. Recently, antibody- and nucleic acid-based pharmaceuticals have increasingly been used to treat retinal diseases, with improvement or cure as the goal; however, these drugs are currently only administered by intravitreal injection. In this study, we present a novel approach to treating retinal diseases using eye drops that contain PnkRNA, a single-stranded RNA nucleic acid. PnkRNA-loaded liposomes were shown to effectively deliver retinal drugs and significantly inhibit retinal thickening in a mouse retinal-vein occlusion model. Cationic modification of the liposome surface enhanced the delivery of nucleic acids and therapeutic efficacy. Moreover, to reduce the frequency of eye-drop administration, liposomes were incorporated into the thermoresponsive gels. This formulation provided sustained retinal delivery and exhibited superior therapeutic efficacy compared with liposomal eye drops. This nucleic acid retinal delivery technology represents a significant advancement in drug-delivery technology, offering a safe and simple treatment for retinal diseases.
Keywords: drug delivery; eye drop; nucleic acid; retina; retinal-vein occlusion; thermoresponsive gel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

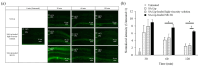
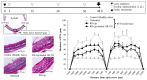
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of inhaler devices in asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease: a systematic review of the literature.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(26):1-149. doi: 10.3310/hta5260. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701099
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 06;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. PMID: 17253490 Updated.
-
Prophylactic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the prevention of macular oedema after cataract surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 1;11(11):CD006683. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006683.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27801522 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Immunogenicity and seroefficacy of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jul;28(34):1-109. doi: 10.3310/YWHA3079. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39046101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bourne R.R.A., Flaxman S.R., Braithwaite T., Cicinelli M.V., Das A., Jonas J.B., Keeffe J., Kempen J.H., Leasher J., Limburg H., et al. Vision loss expert group, magnitude, temporal trends, and projections of the global prevalence of blindness and distance and near vision impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health. 2017;5:888–897. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(17)30293-0. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

