Application of Response Surface Methodology for the Optimization of Basic Red 46 Dye Degradation in an Electrocoagulation-Ozonation Hybrid System
- PMID: 40572589
- PMCID: PMC12195645
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30122627
Application of Response Surface Methodology for the Optimization of Basic Red 46 Dye Degradation in an Electrocoagulation-Ozonation Hybrid System
Abstract
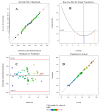
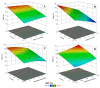
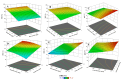
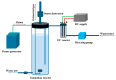
The release of synthetic dyes like Basic Red 46 (BR46) from industrial wastewater has raised growing concerns due to their toxicity, long-term persistence, and resistance to standard biological treatment methods. In this work, we developed and tested a pilot-scale electrocoagulation-ozonation (EC-O) hybrid system aimed at removing BR46 from aqueous solutions. The system integrates electrocoagulation, using iron electrodes, with ozone-based advanced oxidation processes, facilitating a combination of coagulation, adsorption, and oxidative breakdown of dye molecules. The response surface methodology (RSM) with a central composite design (CCD) was applied to optimize the treatment process, focusing on five variables: current density, flow rate, ozone dosage, ozonation time, and initial dye concentration. The quadratic model exhibited strong predictive power, with an adjusted R2 of 0.9897 and a predicted R2 of 0.9812. The optimal conditions identified included a current density of 70 A/m2, flow rate of 1.6 L/min, ozone dose of 2.0 g/h, and an ozonation time of 20 min, achieving a predicted removal efficiency of 91.67% for a solution with BR46 at an initial concentration of 300 mg/L. Experiments conducted under these conditions confirmed the model's reliability, with observed removal rates exceeding 90% and deviations under 2%. The EC-O system had a treatment capability of 26.19 L/h and an energy consumption of 3.04 kWh/m3. These findings suggest that the EC-O system is an effective and scalable option for treating dye-contaminated wastewater, offering faster and more efficient results than conventional techniques.
Keywords: Basic Red 46; azo dye removal; electrocoagulation–ozonation; pilot-scale study; response surface methodology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 14;9(9):CD010216. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010216.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11:CD010216. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010216.pub7. PMID: 34519354 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Effect of ozonation-based disinfection methods on the removal of antibiotic resistant bacteria and resistance genes (ARB/ARGs) in water and wastewater treatment: a systematic review.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Mar 10;811:151404. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151404. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 34767893
References
-
- Saxena A., Gupta S. Innovations in Environmental Biotechnology. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2022. Toxicological Impact of Azo Dyes and Their Microbial Degraded Byproducts on Flora and Fauna; pp. 319–343.
-
- Kataria J., Rawat H., Tomar H., Gaurav N., Kumar A. Azo Dyes Degradation Approaches and Challenges: An Overview. Sci. Temper. 2022;13:384–400. doi: 10.58414/scientifictemper.2022.13.2.56. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

