Accuracy Verification of a Computed Tomography-Based Navigation System for Total Hip Arthroplasty in Severe Hip Dysplasia: A Simulation Study Using 3D-Printed Bone Models of Crowe Types II, III, and IV
- PMID: 40572661
- PMCID: PMC12195199
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina61060973
Accuracy Verification of a Computed Tomography-Based Navigation System for Total Hip Arthroplasty in Severe Hip Dysplasia: A Simulation Study Using 3D-Printed Bone Models of Crowe Types II, III, and IV
Abstract
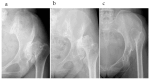
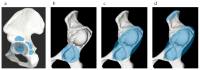
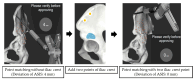
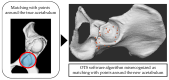
Background and Objective: The use of computed tomography (CT)-based navigation systems has been shown to improve surgical accuracy in total hip arthroplasty. However, there is limited literature available about the application of CT-based navigation systems in severe hip dysplasia. This study aimed to evaluate the accuracy of a CT-based navigation system in patients with severe hip dysplasia using three-dimensional (3D)-printed bone models. Methods: 3D-printed bone models were generated from CT data of patients with severe hip dysplasia (Crowe type II, 10 hips; type III, 10 hips; and type IV, 10 hips). The accuracy of automatic segmentation, success rate, point-matching accuracy across different registration methods, and deviation values at reference points after registration were assessed. Results: For the combined cohort of Crowe II, III, and IV cases (n = 30), the Dice Similarity Coefficient and Jaccard Index were 0.99 ± 0.01 and 0.98 ± 0.02, respectively. These values indicate a high level of segmentation accuracy. The "Matching with true and false acetabulum + iliac crest" method achieved a 100% success rate across all groups, with mean deviations of 0.08 ± 0.28 mm in the Crowe II group, 0.12 ± 0.33 mm in the Crowe III group, and 0.14 ± 0.50 mm in the Crowe IV group (p = 0.572). In the Crowe IV group, the anterior superior iliac spine deviation was significantly lower using the "Matching with true and false acetabulum + iliac crest" method compared to the "Matching with true and false acetabulum" method (0.28 ± 0.49 mm vs. 3.29 ± 2.56 mm, p < 0.05). Conclusions: This study demonstrated the high accuracy of automatic AI-based segmentation, with a Dice Similarity Coefficient of 0.99 ± 0.01 and a Jaccard Index of 0.98 ± 0.02 in the combined cohort of Crowe type II, III, and IV cases (n = 30). The matching success rate was 100%, with additional points on the iliac crest, which improved matching accuracy and reduced deviations, depending on the case.
Keywords: CT-based navigation; Ortoma Treatment Solution; artificial intelligence; bone model; total hip arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sandwich method in Crowe type 4 hip arthroplasty surgery: a retrospective study on a novel technique for osteotomy line union.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jun 13;104(24):e42784. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042784. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40527808 Free PMC article.
-
Computer simulation study of cementless cup placement for dysplastic hip osteoarthritis using subluxation percentage of Crowe classification.J Orthop Res. 2024 Aug;42(8):1801-1809. doi: 10.1002/jor.25819. Epub 2024 Feb 26. J Orthop Res. 2024. PMID: 38409822
-
Total Hip Arthroplasty for Crowe III/IV Hip Dysplasia With Oblique Subtrochanteric Shortening Osteotomy and S-ROM-A Modular Stem: 10-Year Outcomes.Orthop Surg. 2025 Aug 19. doi: 10.1111/os.70154. Online ahead of print. Orthop Surg. 2025. PMID: 40830086
-
Splinting for the non-operative management of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) in children under six months of age.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Oct 10;10(10):CD012717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012717.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36214650 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
References
-
- García-Rey E., Carbonell-Escobar R., Cordero-Ampuero J., García-Cimbrelo E. Outcome of a Hemispherical Porous-Coated Acetabular Component with a Proximally Hydroxyapatite-Coated Anatomical Femoral Component: An Update at 23 to 26 Years’ Follow-Up. Bone Jt. J. 2019;101-B:378–385. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.101B4.BJJ-2018-1223.R1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jacquot L., Machenaud A., Bonnin M.P., Chouteau J., ReSurg, Vidalain J.-P. Survival and Clinical Outcomes at 30 to 35 Years Following Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty with a Cementless Femoral Stem Fully Coated with Hydroxyapatite. J. Arthroplast. 2023;38:880–885. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2022.11.016. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

