Morphofunctional Assessment of Malnutrition and Sarcopenia Using Nutritional Ultrasonography in Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis
- PMID: 40572732
- PMCID: PMC12195185
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina61061044
Morphofunctional Assessment of Malnutrition and Sarcopenia Using Nutritional Ultrasonography in Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis
Abstract
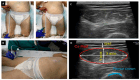
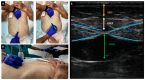
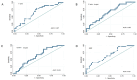
Background and Objectives: Malnutrition and sarcopenia are highly prevalent and clinically impactful conditions in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis (MHD), yet their early detection remains challenging. This study aimed to assess the diagnostic performance of nutritional ultrasonography (NUS) in the morphofunctional evaluation of malnutrition and sarcopenia, and to compare its utility with established tools such as bioimpedance analysis (BIA), biochemical markers, handgrip strength (HGS), and functional performance tests. Materials and Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in 74 stable MHD patients. Clinical, analytical, anthropometric, BIA, NUS, and functional parameters were collected, along with validated nutritional and frailty scales. NUS was used to assess the quadriceps rectus femoris (QRF) and preperitoneal visceral fat (PPVF), measuring Y-axis, Y-axis/height, cross-sectional muscle area rectus femoris (CS-MARF), muscle area rectus femoris index adjusted to height (MARFIh), and supramuscular fat (SMF). Sarcopenia was defined according to the 2019 European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People (EWGSOP) criteria. Results: The prevalence of risk, confirmed, and severe sarcopenia was 24.3%, 40.5%, and 20.3%, respectively. Severe-to-moderate protein-energy wasting (PEW) affected 44.6% of patients. Compared to non-sarcopenic individuals, sarcopenic patients had lower values of HGS, prealbumin, lean body mass, and phase angle. NUS-derived cut-off values for sarcopenia were Y-axis ≤ 8 mm, Y-axis/height ≤ 2.9 mm/m2, CS-MARF ≤ 2.4 cm2, and MARFIh ≤ 0.9 cm2/m2. The most discriminative NUS parameters were Y-axis and SMF (AUC 0.67), followed by Y-axis/height (AUC 0.65) and MARFIh (AUC 0.63). NUS measurements correlated significantly with ASMI, phase angle, HGS, and SPPB scores. Conclusions: Nutritional ultrasonography is a feasible, reproducible, and clinically valuable tool for assessing muscle mass and quality in MHD patients. Its incorporation into routine practice may enhance early detection of malnutrition and sarcopenia, thereby facilitating timely, individualized nutritional interventions.
Keywords: hemodialysis; malnutrition; morphofuntional assessment; nutritional ultrasonography; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests or any other interests that could be perceived to influence the results and/or discussion presented in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
POCUS ultrasound: A tool for the detection and monitoring of sarcopenia in peritoneal dialysis.Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2025 Apr;45(4):302-311. doi: 10.1016/j.nefroe.2025.03.003. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2025. PMID: 40155221
-
Impedance-derived phase angle as an indicator of physical function in maintenance hemodialysis patients.Nutrition. 2025 Aug;136:112795. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2025.112795. Epub 2025 Apr 5. Nutrition. 2025. PMID: 40373354
-
The Role of Diaphragmatic Ultrasound in Identifying Sarcopenia in COPD Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025 Jan 1;20:1-9. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S492191. eCollection 2025. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025. PMID: 39777216 Free PMC article.
-
Global prevalence of sarcopenia and severe sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022 Feb;13(1):86-99. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12783. Epub 2021 Nov 23. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022. PMID: 34816624 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis, prevalence, and mortality of sarcopenia in dialysis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022 Feb;13(1):145-158. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12890. Epub 2022 Jan 5. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022. PMID: 34989172 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rashid I., Bashir A., Tiwari P., D’Cruz S., Jaswal S. Estimates of malnutrition associated with chronic kidney disease patients globally and its contrast with India: An evidence based systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health. 2021;12:100855. doi: 10.1016/j.cegh.2021.100855. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

