Underlying Diagnosis of Food Bolus Obstruction Acute Admissions to Otorhinolaryngology: A Shift to Provide the Best Care as per the Current Guidelines
- PMID: 40572735
- PMCID: PMC12195163
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina61061047
Underlying Diagnosis of Food Bolus Obstruction Acute Admissions to Otorhinolaryngology: A Shift to Provide the Best Care as per the Current Guidelines
Abstract
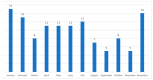
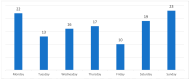
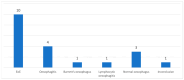
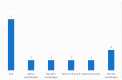
Background and Objectives: In the United Kingdom, some patients with food bolus obstruction (FBO) are admitted under the care of ear, nose, and throat (ENT) doctors. In the literature, eosinophilic oesophagitis (EoE) is the most common cause of FBO. We analysed ENT FBO admissions and interventions used in our hospital to investigate for EoE. Materials and Methods: This paper details a retrospective study of adult FBO admissions to an ENT ward from January 2016 to December 2019 at a single centre. Results: In total, 120 patients were admitted. Half of the patients required instrumentation to resolve the obstruction-31% underwent rigid oesophagoscopy (RO) and 69% oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD). Biopsies were taken during 48% of inpatient OGDs and 5% of ROs. 48% had a histopathological diagnosis of EoE. There was no mention of a specific number of eosinophils per high-power field in 53% of EoE pathology reports. Potentially, some patients were EoE-negative due to an inadequate number of biopsies taken-71% of patients had an insufficient number of biopsies to exclude EoE. A total of 56% of all patients with FBO did not undergo inpatient or outpatient OGDs with biopsies. Conclusions: Biopsies were not taken in all FBO patients undergoing oesophagoscopy, leaving EoE underdiagnosed. Follow-up arrangements were often suboptimal to exclude EoE.
Keywords: biopsy; dysphagia; eosinophilic esophagitis; oesophagogastroduodenoscopy; swallowing disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
R.M. has served on the advisory board on management pathways of food bolus obstruction and eosinophilic oesophagitis organised by Dr. Falk Pharma. M.M. is an advisory board member for Dr. Falk Pharma. A.K. and S.M. declare no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Birk M., Bauerfeind P., Deprez P.H., Häfner M., Hartmann D., Hassan C., Hucl T., Lesur G., Aabakken L., Meining A. Removal of foreign bodies in the upper gastrointestinal tract in adults: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline. Endoscopy. 2016;48:489–496. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-100456. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

