"Pre-Treatment" and "Post-Treatment" Systemic Inflammatory Markers: Is There Any Prognostic Role for Metastatic Cervical Cancer on Bevacizumab Containing Treatment?
- PMID: 40572788
- PMCID: PMC12195193
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina61061100
"Pre-Treatment" and "Post-Treatment" Systemic Inflammatory Markers: Is There Any Prognostic Role for Metastatic Cervical Cancer on Bevacizumab Containing Treatment?
Abstract
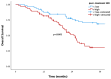
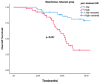
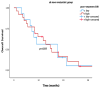
Background and Objectives: Despite developments in cervical cancer (CC) treatment, an advanced stage is a poor prognostic factor. Cervical cancer is an immunogenic tumor in which viruses, like HPV, play a role in carcinogenesis. Therefore, systemic inflammatory markers (SIMs) may have prognostic value. Most studies on SIMs focus on the early stage by evaluating pretreatment levels. This study aims to evaluate the prognostic and predictive values of both pretreatment and post-treatment parameters at the advanced stage, as well as treatment efficacy after progression with first-line treatment. Materials and Methods: A total of 133 advanced-stage CC patients with progression on first-line platin-paclitaxel and bevacizumab were evaluated retrospectively. Demographic and histopathological characteristics were recorded along with treatment details. Pre-treatment baseline blood parameters and post-treatment follow-up values were recorded to calculate SIMs as the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), and systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI). Results: Median values for SIMs were accepted as cut-off values. Post-treatment values demonstrated stronger predictive power, with pre-treatment SIRI and NLR being significant only in univariate analysis, but not in multivariate analysis. High post-treatment SIRI (>2.1) was correlated with shorter overall survival (OS) and considered a poor prognostic factor. High post-treatment SIRI (>2.1), -SII (>746), and -PLR (>197) emerged as independent prognostic factors for progression-free survival (PFS). Their prognostic values were clearer in the whole population and the metachronous metastatic subgroup. Rechallenge of platinum-based chemotherapy was an option for those who had at least 6 months of PFS with first-line platinum-based chemotherapy. Bevacizumab addition to single-agent or combination regimens led to improved ORR as well. Conclusions: Post-treatment SIRI is a promising prognostic factor for OS, while post-treatment SIRI, SII, and PLR may serve as convenient SIMs for PFS. Platinum-based combination chemotherapy reinduction is a feasible second-line treatment strategy, especially with the addition of bevacizumab.
Keywords: bevacizumab; cervix; systemic inflammatory markers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictive value of systemic inflammatory indices for perinatal outcomes following cervical cerclage: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Jul 10;25(1):750. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07888-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 40640782 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Taxane monotherapy regimens for the treatment of recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 12;7(7):CD008766. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008766.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tewari K.S., Sill M.W., Penson R.T., Huang H., Ramondetta L.M., Landrum L.M., Oaknin A., Reid T.J., Leitao M.M., Michael H.E., et al. Bevacizumab for advanced cervical cancer: Final overall survival and adverse event analysis of a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial (Gynecologic Oncology Group 240) Lancet. 2017;390:1654–1663. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31607-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Q., Zhai B., Li J., Wang H., Liu Z., Shi R., Wu H., Xu Y., Ji S. Systemic immune-inflammatory index predict short-term outcome in recurrent/metastatic and locally advanced cervical cancer patients treated with PD-1 inhibitor. Sci. Rep. 2024;14:31528. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82976-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kitagawa R., Katsumata N., Shibata T., Kamura T., Kasamatsu T., Nakanishi T., Nishimura S., Ushijima K., Takano M., Satoh T., et al. Paclitaxel Plus Carboplatin Versus Paclitaxel Plus Cisplatin in Metastatic or Recurrent Cervical Cancer: The Open-Label Randomized Phase III Trial JCOG0505. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015;33:2129–2135. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.4391. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical