Integrating Traditional Nutritional Wisdom into Digital Nutrition Platforms: Toward Culturally Adaptive and Inclusive Health Technologies
- PMID: 40573089
- PMCID: PMC12196328
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17121978
Integrating Traditional Nutritional Wisdom into Digital Nutrition Platforms: Toward Culturally Adaptive and Inclusive Health Technologies
Abstract
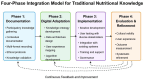
Background/Objectives: Traditional nutritional knowledge, shaped by centuries of cultural and ecological adaptation, offers holistic and sustainable dietary frameworks that remain highly relevant to modern health challenges. However, current digital nutrition platforms often fail to reflect this diversity, relying instead on standardized models with limited cultural sensitivity. This paper aims to explore how traditional nutritional wisdom can be integrated into digital health platforms to promote more inclusive and effective approaches to personalized nutrition. Methods: This perspective paper employs a cultural adaptation framework to analyze the integration of traditional food knowledge into digital contexts. Drawing from interdisciplinary research across nutrition science, anthropology, digital health and implementation science, we utilize the Knowledge-to-Action (KTA) Framework and the PEN-3 Cultural Model to structure our analysis. A systematic scoping review of literature published between 2010 and 2025 was conducted to identify integration challenges and opportunities. Additionally, we analyzed case studies of three traditional dietary systems (Argentina, Italy and Japan) and evaluated five leading digital nutrition platforms for their degree of cultural inclusivity, using qualitative comparative methods. Results: The analysis highlights significant challenges in adapting traditional knowledge to digital formats, including standardization barriers, contextual loss and technological limitations. However, successful integration initiatives demonstrate that through participatory design, flexible data architectures and culturally-informed algorithms, traditional food systems can be meaningfully represented. Our proposed four-phase integration framework-documentation, digital adaptation, implementation and evaluation-provides a structured approach for developers and researchers. Conclusions: Bridging traditional nutrition with digital platforms represents a vital opportunity to enhance personalization and preserve food heritage while improving health outcomes for diverse populations. This integration requires interdisciplinary collaboration, user-centered design processes and ethical approaches that respect cultural ownership and context.
Keywords: Indigenous knowledge; cultural adaptation; cultural sustainability; digital nutrition; digital storytelling; eHealth; generative AI; health equity; knowledge translation; nutrition informatics; nutrition technology; participatory methods; personalized nutrition; traditional food systems; user-centred design.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accreditation through the eyes of nurse managers: an infinite staircase or a phenomenon that evaporates like water.J Health Organ Manag. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1108/JHOM-01-2025-0029. Online ahead of print. J Health Organ Manag. 2025. PMID: 40574247
-
Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314
-
How to Implement Digital Clinical Consultations in UK Maternity Care: the ARM@DA Realist Review.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025 May;13(22):1-77. doi: 10.3310/WQFV7425. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025. PMID: 40417997 Review.
-
Consumers' and health providers' views and perceptions of partnering to improve health services design, delivery and evaluation: a co-produced qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 14;3(3):CD013274. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013274.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36917094 Free PMC article.
-
Factors that impact on the use of mechanical ventilation weaning protocols in critically ill adults and children: a qualitative evidence-synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 4;10(10):CD011812. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011812.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27699783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afshin A., Babalola D., Mclean M., Yu Z., Ma W., Chen C.-Y., Arabi M., Mozaffarian D. Information Technology and Lifestyle: A Systematic Evaluation of Internet and Mobile Interventions for Improving Diet, Physical Activity, Obesity, Tobacco and Alcohol Use. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016;5:e003058. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.003058. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bomfim R.A., Forster D., Kirkham-Ali K., Niyonzima N., Siegel K.R., Micha R., Diez Roux A.V., Bhavsar N.A., Boakye E., Spring B., et al. Limited cultural representation in mobile health apps for diet and nutrition. Digit. Health. 2023;9:20552076231175138.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources