Effects of Intermittent Fasting and Calorie Restriction on Exercise Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40573103
- PMCID: PMC12195750
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17121992
Effects of Intermittent Fasting and Calorie Restriction on Exercise Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
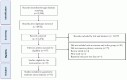
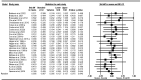
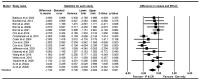
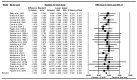
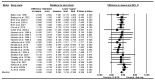
Context: Intermittent fasting (IF) and calorie restriction (CR) have gained interest as dietary strategies due to their potential for weight loss and multiple metabolic benefits. These strategies are often accompanied by exercise in an attempt to improve body composition and physical performance. However, further research is crucial to understanding whether or not physical performance is affected by the expected weight loss and related body composition changes in individuals on IF and CR, even when exercise is combined. Objective: We aimed to systematically evaluate the effects of IF and CR on exercise performance and body composition in adults aged 18 to 65 years. Data Source: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement. A systematic review was conducted up to April 2024 by searching electronic databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus. There was no limit on publication dates. Data Extraction: The search explored the impact of IF and CR combined with exercise vs. exercise alone (control) on exercise performance outcomes: VO2max, handgrip strength, bench press strength, knee extensor strength, leg press strength, countermovement jump (CMJ), 400 m walk test, and gait speed; body weight, body mass index (BMI), and body composition: fat-free mass (FFM), fat mass (FM), and body fat percentage (BFP). Analyses included calculation of weighted mean difference (WMD), standardized mean difference (SMD), and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) to assess outcomes. Data Analysis: The meta-analysis included a total of 35 studies, ranging from 4 to 52 weeks and involving 1266 participants. The results showed that IF (hypocaloric or eucaloric diet) and CR combined with exercise increased handgrip strength [WMD = 1.707 kg, p = 0.01] compared to exercise alone. Moreover, IF and CR combined with exercise did not significantly affect VO2max [SMD = 0.005, p = 0.94], bench press strength [WMD = 0.377 kg, p = 0.778], knee extensor strength [WMD = -4.729 kg, p = 0.12], leg press strength [WMD = -2.874 kg, p = 0.415], countermovement jump [WMD = -0.226 cm, p = 0.80], 400 m walk test performance [WMD = -8.794 s, p = 0.06], or gait speed [WMD = 0.005 m/s, p = 0.82] compared to exercise alone. Moreover, IF and CR combined with exercise decreased body weight [WMD = -4.375 kg, p = 0.001], BMI [WMD = -1.194 kg·m-2, p = 0.001], FFM [WMD = -1.653 kg, p = 0.001], FM [WMD = -2.858 kg, p = 0.001], BFP [WMD = -0.826%, p = 0.001] compared to exercise alone. Conclusions: IF (hypocaloric or eucaloric) and CR can be effectively integrated into exercise training without negatively impacting most measures of physical performance, while significantly enhancing weight loss and adiposity-related outcomes. The findings from this meta-analysis involving both athletes and non-athletes suggest that weight loss induced by IF and CR combined with exercise does not necessarily result in reduced physical performance. In real-world scenarios, however, different outcomes are conceivable, as body composition, physical capacity, diet and exercise can vary considerably based on individual conditions.
Keywords: body composition; calorie restriction; exercise performance; intermittent fasting; muscle strength.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Effects of Different Exercises Combined with Different Dietary Interventions on Body Composition: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 5;16(17):3007. doi: 10.3390/nu16173007. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39275322 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of intermittent fasting on body composition and cardiometabolic health in adults with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024 Sep;26(9):3830-3841. doi: 10.1111/dom.15730. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024. PMID: 38956175
-
Longer-term effects of intermittent fasting on body composition and cardiometabolic health in adults with overweight and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Obes Rev. 2025 Feb;26(2):e13855. doi: 10.1111/obr.13855. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Obes Rev. 2025. PMID: 39501676
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3(3):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030386 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional supplementation for stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD000998. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000998.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Santos H.O. Intermittent fasting and fat mass: What is the clinical magnitude? Obesities. 2022;2:1–7. doi: 10.3390/obesities2010001. - DOI
-
- Elortegui Pascual P., Rolands M.R., Eldridge A.L., Kassis A., Mainardi F., Lê K.A., Karagounis L.G., Gut P., Varady K.A. A Meta-Analysis comparing the effectiveness of alternate day fasting, the 5, 2 diet, and Time-Restricted eating for weight loss. Obesity. 2023;31:9–21. doi: 10.1002/oby.23568. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

