Awareness of Eating Disorders, Nutritional Knowledge, and Emotionally Driven Eating Among Polish Adolescents Aged 15-17-A Pilot Study
- PMID: 40573104
- PMCID: PMC12195971
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17121994
Awareness of Eating Disorders, Nutritional Knowledge, and Emotionally Driven Eating Among Polish Adolescents Aged 15-17-A Pilot Study
Abstract
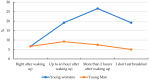
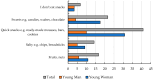
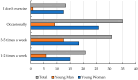
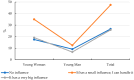
Background/Objectives: Despite the growing awareness of nutrition and the popularity of healthy lifestyles among adolescents, disordered eating behaviors-such as anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, binge eating disorder (BED), and avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID)-remain significant public health concerns. ARFID, officially recognized only in 2013, is still poorly understood among youth. This study aimed to assess the relationship between adolescents' nutritional knowledge, emotional regulation, media influence, and eating behaviors. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in 2024 among 120 students aged 15-17 attending W. Reymont Secondary School No. II in Ostrów Wielkopolski, Poland. Participants completed a custom-designed, paper-based questionnaire consisting of 30 single-choice questions and demographic items. The instrument assessed knowledge of eating disorders, body satisfaction, social media impact, and the emotional determinants of food choices. The tool was developed with expert input but has not undergone formal psychometric validation. While many adolescents demonstrated basic nutritional knowledge-such as awareness of BMI norms and food group distribution-they often failed to apply this knowledge to their dietary behaviors. Results: Significant gender differences were observed: girls were more likely to restrict food intake, report emotional eating, and engage in slimming behaviors, while boys were less emotionally reactive and less influenced by social media. Most participants reported eating one meal daily with family but rarely discussed nutrition at home. Emotional involvement in eating, particularly among girls, emerged as a key factor, more influential than social media in shaping dietary behaviors. Conclusions: The findings highlight a clear gap between nutritional knowledge and actual behavior among adolescents, driven in part by emotional dysregulation and body image concerns. School-based interventions should incorporate not only nutritional education but also emotional regulation strategies and media literacy to effectively support healthy eating behaviors in youth.
Keywords: adolescent awareness; eating disorders; prevalence of disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emotion regulation as a transdiagnostic construct across the spectrum of disordered eating in adolescents: A systematic review.J Affect Disord. 2025 Jan 15;369:868-885. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.10.017. Epub 2024 Oct 16. J Affect Disord. 2025. PMID: 39424149
-
Awareness of the Connection Between Food and Nutrition in Adolescents: A Pilot Study.Nutrients. 2025 Jun 6;17(12):1949. doi: 10.3390/nu17121949. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40573060 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional interventions for survivors of childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 22;2016(8):CD009678. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009678.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27545902 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Feeding Challenges in Trisomy 21: Prevalence and Characteristics of Feeding Disorders and Food Neophobia-A Cross-Sectional Study of Polish Children and Adolescents with Down Syndrome.Nutrients. 2025 Jun 18;17(12):2030. doi: 10.3390/nu17122030. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40573140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Skolmowska D., Głąbska D., Guzek D. Relationship between food preferences and eating habits during the COVID-19 pandemic among Polish adolescents (PLACE-19 Study) Nutrients. 2021;13:2640.
-
- Friedman V.J., Wright C.J., Molenaar A., McCaffrey T., Brennan L., Lim M.S. The use of social media as a persuasive platform to facilitate nutrition and health behavior change in young adults: Web-based conversation study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022;24:e28063. doi: 10.2196/28063. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ciborowska H., Rudnicka A. Żywienie Zdrowego i Chorego Człowieka. PZWL; Warszawa, Poland: 2007. Dietetyka.
-
- Jarosz M., Rychlik E., Stoś K., Charzewska J. Normy Żywienia dla Populacji Polski i ich Zastosowanie. Narodowy Instytut Zdrowia Publicznego—Państwowy Zakład Higieny; Warsaw, Poland: 2020. p. 83.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous