Protective Effect of Biobran/MGN-3, an Arabinoxylan from Rice Bran, Against the Cytotoxic Effects of Polyethylene Nanoplastics in Normal Mouse Hepatocytes: An In Vitro and In Silico Study
- PMID: 40573105
- PMCID: PMC12195903
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17121993
Protective Effect of Biobran/MGN-3, an Arabinoxylan from Rice Bran, Against the Cytotoxic Effects of Polyethylene Nanoplastics in Normal Mouse Hepatocytes: An In Vitro and In Silico Study
Abstract
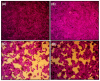
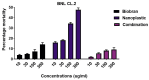
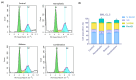
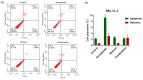
Background: Plastic is one of the most versatile and widely used materials, but the environmental accumulation of nanoplastics (NPs) poses a risk to human health. Preclinical studies have verified that the liver is one of the main organs susceptible to NPs. Biobran/MGN-3, an arabinoxylan from rice bran, has been shown to have hepatoprotective effects; here, we show Biobran's ability to alleviate polyethylene nanoplastics (PE-NPs)-induced liver cell toxicity by reversing apoptosis and restoring G2/M cell arrest in mouse liver cells (BNL CL.2).
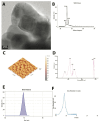
Methods: Toxicological effects were measured using the sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay for cell viability and flow cytometry for cell cycle analysis and apoptosis. An in silico study was also used to demonstrate the docking of PE-NPs to pro-inflammatory mediator proteins (IL-6R, IL-17R, CD41/CD61, CD47/SIRP), cell cycle regulators (BCL-2, c-Myc), as well as serine carboxypeptidase, which is an active ingredient of Biobran.
Results: Exposing liver cells to PE-NPs caused a significant decrease in cell viability, with an IC50 value of 334.9 ± 2.7 µg/mL. Co-treatment with Biobran restored cell viability to normal levels, preserving 85% viability at the highest concentration of PE-NPs. Additionally, total cell death observed after exposure to PE-NPs was reduced by 2.4-fold with Biobran co-treatment. The G2/M arrest and subsequent cell death (pre-G0 phase) induced by PE-NPs were normalized after combined treatment. The in silico study revealed that Biobran blocks the nucleophilic centers of PE-NPs, preventing their interaction with pro-inflammatory mediators and cell cycle regulators.
Conclusions: These findings highlight the potential use of Biobran as a hepatoprotector against NP toxicity.
Keywords: Biobran; G2/M cell arrest; MGN-3; apoptosis; hepatocytes; polyethylene nanoplastics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Selenium for preventing cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 29;1(1):CD005195. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005195.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29376219 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab for adults with Hodgkin's lymphoma (a rapid review using the software RobotReviewer).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 12;7(7):CD012556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30001476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Plastics—The fast Facts 2023. [(accessed on 1 April 2025)]. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-fast-facts-2023/
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

