Exploring the Role of Intrinsic Motivation in Healthy Eating Intentions: An Extension of the Theory of Planned Behavior in Chinese Adults
- PMID: 40573118
- PMCID: PMC12196538
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17122007
Exploring the Role of Intrinsic Motivation in Healthy Eating Intentions: An Extension of the Theory of Planned Behavior in Chinese Adults
Abstract
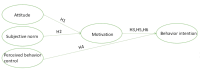
Background: Unhealthy diets are a leading cause of obesity, which increases the risk of chronic diseases such as hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions. The theory of planned behavior (TPB) explains eating intentions through attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control (PBC), yet these constructs may not fully account for the complexity of intention formation. Motivation has been identified as a stronger predictor of the maintenance of long-term healthy behaviors. This study extends the TPB by introducing motivation as a mediating variable to examine whether attitudes and subjective norms influence motivation, which in turn affects behavioral intention. Methods: An online survey was conducted between 2019 and 2023, collecting responses from 2114 adults residing in Beijing, Shanghai, and selected regions of Anhui, Daqing, and Henan. Structural equation modeling (SEM) was employed to examine the relationships among the TPB constructs, motivation, and behavioral intention. Results: SEM analysis revealed significant associations between attitude and subjective norms with motivation. Additionally, motivation and PBC were significantly associated with behavioral intention. Motivation was found to mediate the relationships between attitude and intention (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.004-0.021, p = 0.004) and subjective norms and intention (95% CI: 0.013-0.035, p = 0.012). Conclusions: These findings suggest that attitudes and subjective norms enhance motivation for healthy eating among Chinese adults. In turn, motivation-along with PBC-plays a key role in predicting behavioral intention. Future research should further explore the mediating role of motivation in shaping healthy eating intentions within the TPB framework.
Keywords: Chinese adults; behavior; healthy eating; motivation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Influencing factors and mechanisms promoting proactive health behavior intention: an integration of the health belief model and the theory of planned behavior.Front Public Health. 2025 Jul 10;13:1629046. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1629046. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40709034 Free PMC article.
-
Consumers' motivation to purchase electric vehicles: a mixed-methods belief elicitation study using theory of planned behavior.Acta Psychol (Amst). 2025 Aug;258:105185. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2025.105185. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Acta Psychol (Amst). 2025. PMID: 40541135
-
Determinants of fruit and vegetable consumption among Saudi adults: an extended Theory of Planned Behavior approach.Front Public Health. 2025 Aug 19;13:1593625. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1593625. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40904927 Free PMC article.
-
Applying the theory of planned behavior to examine breastfeeding determinants in countries of the Gulf Cooperation Council: a systematic review.Int Breastfeed J. 2025 May 30;20(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13006-025-00739-z. Int Breastfeed J. 2025. PMID: 40448088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The theory of planned behaviour and discrete food choices: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2015 Dec 30;12:162. doi: 10.1186/s12966-015-0324-z. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2015. PMID: 26715190 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stewart H., Yen S.T. Changing household characteristics and the away-from-home food market: A censored equation system approach. Food Policy. 2004;29:643–658. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2004.10.003. - DOI
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

