Arecoline Triggers Psychostimulant Responses by Modulating the Intestinal Microbiota to Influence Neurotransmitter Levels and Digestive Enzyme Activity
- PMID: 40573191
- PMCID: PMC12196527
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18060794
Arecoline Triggers Psychostimulant Responses by Modulating the Intestinal Microbiota to Influence Neurotransmitter Levels and Digestive Enzyme Activity
Abstract
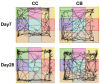
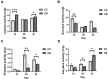
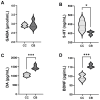
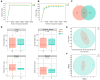
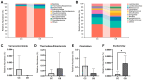
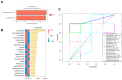
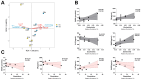
Background:Areca catechu L. is an evergreen tree belonging to the Arecaceae family. As an important traditional Chinese medicine, it has wide applications in the field of herbal medicine. Arecoline is the main active component responsible for its medicinal effects and plays a key role in its central nervous system (CNS) stimulant properties. Methods: This study investigated the excitatory effects of arecoline by analyzing behavioral changes in mice, neurotransmitter levels, the intestinal microbiota composition, and enzymatic activities. We further explored the bidirectional interactions between the intestinal microbial ecosystem and the nervous system following arecoline exposure. Results: Arecoline administration significantly increased the activity time ratio in mice (p < 0.05). It also elevated fecal lactase and amylase activities (p < 0.05), suggesting enhanced carbohydrate metabolism that may be one of the reasons for the increased activity time of mice. Serum analysis showed decreased 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT, p < 0.05), increased dopamine (DA) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels (p < 0.001), and no significant change in γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). These findings suggest that arecoline may also play a role in modulating neurotransmitter balance. At the genus level, Escherichia was significantly enriched and positively correlated with DA, BDNF, and GABA, while Clostridium abundance decreased and was positively correlated with 5-HT. Conclusions: Arecoline administration altered multiple enzymatic activities and the microbial composition abundance in the mouse intestine, eliciting psychostimulant effects while maintaining neurotransmitter homeostasis. This study provides an experimental foundation for further pharmacological exploitation of arecoline.
Keywords: Areca catechu L.; arecoline; enzyme activity; intestinal microbiota; neurotransmitters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cheng H.L., Chang W.T., Hu Y.C., Hsieh B.S., Huang T.C., Chong I.W., Huang L.-W., Chang K.-L. Arecoline Increases Glycolysis and Modulates pH Regulator Expression in HA22T/VGH Hepatoma Cells, Leading to Increase of Intracellular Ca2+, Reactive Oxygen Species, and Anoikis. J. Cancer. 2017;8:3173–3182. doi: 10.7150/jca.20523. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

