Wound-Healing Potential of Myristica fragrans Essential Oil: A Multi-Targeted Approach Involving Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis Regulation
- PMID: 40573275
- PMCID: PMC12195913
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18060880
Wound-Healing Potential of Myristica fragrans Essential Oil: A Multi-Targeted Approach Involving Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis Regulation
Abstract
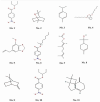
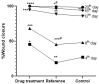
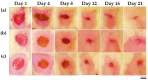
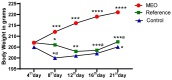
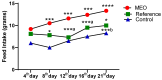
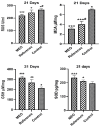
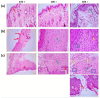
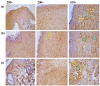
Background: Essential oils are widely studied for their therapeutic potential, including their role in wound healing. Myristica fragrans essential oil (MEO) has been previously investigated for various pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects. However, its mechanistic role in accelerating wound healing and modulating critical pathways, such as oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis, remains poorly characterized. MEO contains a rich profile of monoterpene esters, sesquiterpenoids, and phenolic acids, which may contribute to its bioactivity through unique multi-targeted mechanisms. Objective: This research aims to investigate the curative properties of MEO on wound repair, specifically its capacity to regulate inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in an excision wound model using Wistar rats. Methods: Chemical characterization via GC-MS analysis identified Nitrobenzoate Esters (12.85%), Terpenoid/Cineole (6.99%), and Gamma-Terpinene (4.67%) as the dominant constituents. This study utilized a full-thickness excision wound model, and wound contraction, inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β and TNF-α), a macrophage cell surface marker (CD68), oxidative stress markers (ROS MDA, SOD, GSH), and apoptotic regulation (Caspase-3) was evaluated using macroscopic, histopathological, and immunohistochemical analyses. Result: MEO treatment significantly reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β (658.3 ± 32.7 pg/mg, *** p < 0.005) and TNF-α (266.7 ± 33.3 pg/mg, *** p < 0.005), compared to the control group (983.3 ± 60.1 and 650 ± 42.8 ** p < 0.05, respectively). CD68 expression was also markedly decreased (12.67 ± 0.71 ng/mL, *** p < 0.005). Furthermore, MEO effectively attenuated oxidative stress by reducing ROS and MDA levels while restoring antioxidant enzymes GSH and SOD. Conclusions: This study demonstrates that Mace Essential Oil (MEO) effectively promotes wound healing by modulating inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in a preclinical rat model. Its unique bioactive components suggest significant therapeutic potential as a botanical agent for skin repair. Further research is warranted to explore its application in advanced wound-care formulations.
Keywords: Myristica fragrans; essential oil; mace oil; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that there are no potential conflicts of interest in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of ARA290 in counteracting cadmium-triggered neurotoxicity in PC12 cells.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025 Feb 17;14(1):tfaf023. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfaf023. eCollection 2025 Feb. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025. PMID: 39968520
-
Hydroxysafflor yellow A alleviates oxidative stress and inflammatory damage in the livers of mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and modulates gut microbiota.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 6;16:1568608. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1568608. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40548050 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Antenatal maternal education for improving postnatal perineal healing for women who have birthed in a hospital setting.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 4;12(12):CD012258. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012258.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29205275 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of subdermal adipose derived stem cell injections and early excision on systemic oxidative stress and wound healing in rats with severe scald burns.Burns. 2024 Nov;50(8):2056-2069. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2024.07.037. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Burns. 2024. PMID: 39127577
References
-
- Sujatha P.S., Pavithran S., Sujatha P.S. Wound Healing Effect of Furfural and Pentadecanal from Lagerstroemia speciosa (L.) Pers Acetone Flower extracts against Haemadipsa sylvestris Bite. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 2024;15:12–15.
-
- Pereira Beserra F., Sergio Gushiken L.F., Vieira A.J., Augusto Bérgamo D., Luísa Bérgamo P., Oliveira de Souza M., Alberto Hussni C., Kiomi Takahira R., Henrique Nóbrega R., Monteiro Martinez E.R., et al. From inflammation to cutaneous repair: Topical application of lupeol improves skin wound healing in rats by modulating the cytokine levels, NF-κB, Ki-67, growth factor expression, and distribution of collagen fibers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:4952. doi: 10.3390/ijms21144952. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

