Biosynthesis of Camphane Volatile Terpenes in Amomum villosum Lour: Involved Genes and Enzymes
- PMID: 40573755
- PMCID: PMC12197307
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14121767
Biosynthesis of Camphane Volatile Terpenes in Amomum villosum Lour: Involved Genes and Enzymes
Abstract
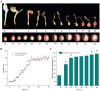
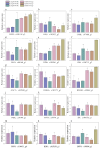
Amomum villosum (A. villosum) Lour., a medicinal species of the Zingiberaceae family, is used for medical purposes. Bornyl acetate, camphor, and borneol are the main bioactive ingredients in A. villosum fruit, and the amount of bornyl acetate is regarded as a measure of the fruit's quality. In order to explore the major effective genes regulating the biosynthesis of camphane volatile terpenes in A. villosum, some DEGs involved in camphane volatile terpene biosynthesis and transcription factors were analyzed and summarized in this study. The result showed that the content of bornyl acetate was altered in the different growth stages. In particular, the significant change occurred from 7 to 30 DAP (days after pollination). The content of bornyl acetate at 30 DAP was 169.3% more than that at 7 DAP. In total, 4782 up-regulated and 5284 down-regulated unigenes were found in G2 vs. G1, as well as 3324 up-regulated and 5036 down-regulated unigenes in G3 vs. G1, and 3332 up-regulated and 4490 down-regulated unigenes in G3 vs. G2. A total of 323 up-regulated and 820 down-regulated unigenes were shared in three growth stage comparisons. We screened the genes that encode the enzymes most likely to inhibit bornyl diphosphate synthase, borneol dehydrogenase, and BAHD acyltransferases. Interestingly, we found that borneol dehydrogenase and bornyl diphosphate synthase displayed bi-substrate features, suggesting that a substrate of catalyzation is promiscuity in the biosynthesis downstream pathway, and the unknown bornyl pyrophosphate hydrolase may not be the specific enzyme for borneol formation. Additionally, the DXR, HDS, and IDS found in the PPI network would assist in the understanding of molecular regulation. The results of this study constructed DGE libraries and identified key genes related to camphane volatile terpenes, which laid a foundation for a deep investigation of the mechanism of volatile terpene biosynthesis, and provided a reference for mining other key genes in A. villosum fruits.
Keywords: biosynthesis pathway; camphane volatile terpenes; transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
References
-
- Zhao H., Li M., Zhao Y., Lin X., Liang H., Wei J., Wei W., Ma D., Zhou Z., Yang J. A Comparison of Two Monoterpenoid Synthases Reveals Molecular Mechanisms Associated With the Difference of Bioactive Monoterpenoids Between Amomum villosum and Amomum longiligulare. Front. Plant Sci. 2021;12:695551. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.695551. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang F., Li X., Lan L., Wang J., Guo P., Sun G. Simultaneous determination of eight components in Amomum villosum and its overall qualityconsistency evaluation by four-dimensional fingerprints assisted with antioxidant activity. J. Chromatogr. A. 2022;1674:463135. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2022.463135. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tu X., Liu Y., Yao Y., Li W., Lou P., Du L., He J., Jian-Neng L. Effects of four drying methods on Amomum villosum Lour. “Guiyan1” volatile organic compounds analyzed via headspace solid phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry coupled with OPLS-DA. RSC Adv. 2022;12:26485–26496. doi: 10.1039/D2RA04592C. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

