Conditional QTL Analysis and Fine Mapping for Thousand-Kernel Weight in Common Wheat
- PMID: 40573836
- PMCID: PMC12196731
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14121848
Conditional QTL Analysis and Fine Mapping for Thousand-Kernel Weight in Common Wheat
Abstract
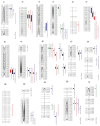
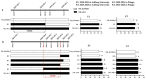
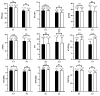
To elucidate the genetic basis of thousand-kernel weight (TKW) related to fundamental traits such as kernel length (KL), kernel width (KW), and kernel diameter ratio (KDR) at the individual quantitative trait loci (QTL) level, both unconditional QTL analysis and conditional QTL analysis for TKW were analyzed using a recombinant inbred line (RIL) population, along with a simplified physical map. A total of 37 unconditional QTLs and 34 conditional QTLs were identified. Six QTLs exhibited independent effects from individual traits (KL, KW, or KDR), while 18 QTLs showed common influences from two or three of these traits simultaneously. Additionally, 26 pairs of epistatically interacting QTLs involving 16 loci were detected. Subsequently, fine mapping of the stable and major-effect QTL QTkw1B was carried out using the derived near-isogenic lines (NILs), ultimately locating it within the interval of 698.15-700.19 Mb on chromosome 1B of the KN9204 genome. The conditional QTL analysis and genetic effect analysis based on NILs both indicated that the increase in TKW was primarily contributed by kernel length. The QTL identified in the present study through the combination of conditional and unconditional QTL mapping could increase the understanding of the genetic interrelationships between TKW and kernel size traits at the individual QTL level and provide a theoretical basis for subsequent candidate gene mining.
Keywords: conditional QTL; fine mapping; thousand-kernel weight; unconditional QTL; wheat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of quantitative trait loci and candidate genes underlying kernel traits of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in response to drought stress.Theor Appl Genet. 2025 Aug 19;138(9):216. doi: 10.1007/s00122-025-05001-y. Theor Appl Genet. 2025. PMID: 40828177
-
Unconditional and conditional QTL analysis of kernel weight related traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in multiple genetic backgrounds.Genetica. 2014 Aug;142(4):371-9. doi: 10.1007/s10709-014-9781-6. Epub 2014 Jul 25. Genetica. 2014. PMID: 25060952
-
Quantitative trait locus mapping for salt and drought tolerance traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):787. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06774-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40596820 Free PMC article.
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
References
-
- Acreche M.M., Slafer G.A. Grain weight response to increases in number of grains in wheat in a Mediterranean area. Field Crops Res. 2005;98:52–59. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2005.12.005. - DOI
-
- Guan P., Di N., Mu Q., Shen X., Wang Y., Wang X., Yu K., Song W., Chen Y., Xin M., et al. Use of near-isogenic lines to precisely map and validate a major QTL for grain weight on chromosome 4AL in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019;132:2367–2379. doi: 10.1007/s00122-019-03359-4. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

