The Impact of Essential Oils Derived from Citrus Species to Control Botrytis cinerea and Their Potential Physiological Actions
- PMID: 40573847
- PMCID: PMC12196830
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14121859
The Impact of Essential Oils Derived from Citrus Species to Control Botrytis cinerea and Their Potential Physiological Actions
Abstract
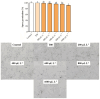
Botrytis cinerea is one of the phytopathogenic fungi of the greatest economic importance worldwide. Essential oils (EOs) have been proposed as a sustainable alternative to reduce the growth of phytopathogenic fungi. Nevertheless, few studies exist about its mechanisms of action. This study evaluated the antifungal activity of EOs from Citrus reticulata, Citrus limon, Citrus sinensis, and Citrus paradisi peels and their encapsulation inside solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs). Accordingly, Citrus EOs were mainly constituted by monoterpene hydrocarbons, where limonene was the most abundant in all EOs. C. reticulata and C. limon EOs reduced the mycelial growth at above 54% after 96 h. The other EOs did not significantly impact the phytopathogen. C. reticulata EO increased the hyphae damage by 40%, but the spore germination was reduced by only 8.34%. It also significantly increased the pH, the electrical conductivity, and the release of intracellular absorbing material and soluble proteins in B. cinerea cultures. Contrary, the esterase, mitochondrial, and succinate dehydrogenase activities decreased at above 50%. C. reticulata EO into SLN reduced the mycelial growth of B. cinerea by 90-97%. These results show that the EO of C. reticulata alters the physiological and metabolic activities of B. cinerea to reduce its growth.
Keywords: Botrytis cinerea; citrus essential oil; physiological mechanisms; solid lipid nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


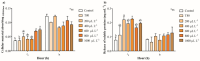


Similar articles
-
Effects of Three Essential Oil Fumigation Treatments on the Postharvest Control of Botrytis cinerea and Their Efficacy as Preservatives of Cherry Tomatoes.Plant Dis. 2023 Jun;107(6):1874-1882. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-09-22-2134-RE. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Plant Dis. 2023. PMID: 36480731
-
The mechanistic insights of essential oil of Mentha piperita to control Botrytis cinerea and the prospection of lipid nanoparticles to its application.Microbiol Res. 2024 Sep;286:127792. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2024.127792. Epub 2024 May 29. Microbiol Res. 2024. PMID: 38852300
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapy for Gaucher's disease: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Jul;10(24):iii-iv, ix-136. doi: 10.3310/hta10240. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16796930
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

