Genome-Wide Analysis of Soybean Polyamine Oxidase Genes Reveals Their Roles in Flower Development and Response to Abiotic Stress
- PMID: 40573854
- PMCID: PMC12196569
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14121867
Genome-Wide Analysis of Soybean Polyamine Oxidase Genes Reveals Their Roles in Flower Development and Response to Abiotic Stress
Abstract
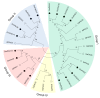
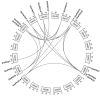
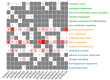
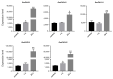
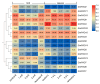
Polyamine oxidase (PAO) is an important enzyme that functions in the catabolism of polyamines. While plant PAOs have been studied in several species, there is a lack of research on this gene family in soybean (Glycine max L.), one of the major food crops worldwide. Here, a genome-wide analysis identified 16 GmPAOs from the soybean genome, which were unevenly distributed in nine soybean chromosomes and were then phylogenetically classified into three groups. Collinearity analysis identified 17 duplicated gene pairs from the GmPAO family, and their Ka/Ks values were all less than one, indicating that the GmPAO family has undergone purifying selection during evolution. Analyses of the conserved motif and gene structure revealed the sequence differences among the GmPAOs of the three groups, suggestive of their functional differentiation. Additionally, the prediction of the secondary and tertiary structure of the GmPAOs provided a further basis for revealing their biological functions. A number of cis-acting elements relevant to development, phytohormone, and stress response were discovered in the promoter regions of the GmPAOs, which might be responsible for their functional diversities. Expression pattern analysis indicated that more than half of the GmPAOs showed preference in flower, two showed specificity in stem and shoot apical meristem, whereas four were barely expressed in all samples. Expression profiling of the GmPAOs also revealed that they were involved in the response to abiotic stresses, including cold, drought, and especially submergence stress. All these results lay an important foundation for further characterizing the functional roles of GmPAOs in soybean development and response to abiotic stresses.
Keywords: Glycine max L.; PAO; bioinformatic analysis; stress response; tissue-specific expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and functional characterization of magnesium transporter (MGT) gene family in soybean (Glycine max L.) and their expression profiles in response to aphid infestation, dehydration, and salt stresses.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 29;20(8):e0330440. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0330440. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40880367 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genomic Analysis of COMT Family Genes in Three Vitis Species Reveals Evolutionary Relationships and Functional Divergence.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jul 7;14(13):2079. doi: 10.3390/plants14132079. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40648090 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of POD gene family and expression differentiation under NaCl, H2O2 and PEG stresses in sorghum.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jul 17;26(1):674. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11858-6. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40676507 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
References
-
- Clay N.K., Nelson T. Arabidopsis thickvein mutation affects vein thickness and organ vascularization, and resides in a provascular cell-specific spermine synthase involved in vein definition and in polar auxin transport. Plant Physiol. 2005;138:767–777. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.055756. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 32201730/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- XLYC2203070/LiaoNing Revitalization Talents Program
- 2024- MSLH-506/Science and Technology Plan Joint Project Natural Science Foundation-General Program of Liao-ning Province
- QCJJ2022-44/the funding project of Northeast Geological S&T Innovation Center of China Geological Survey
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

