Rational Design and Immunological Mechanisms of Circular RNA-Based Vaccines: Emerging Frontiers in Combating Pathogen Infection
- PMID: 40573894
- PMCID: PMC12197763
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines13060563
Rational Design and Immunological Mechanisms of Circular RNA-Based Vaccines: Emerging Frontiers in Combating Pathogen Infection
Abstract
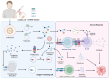
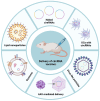
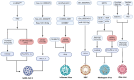
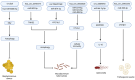
Vaccines remain one of the most effective tools in combating infectious diseases, though traditional platforms are constrained by limitations including suboptimal immunogenicity, safety concerns, and manufacturing complexity. Circular RNA (circRNA) vaccines have recently emerged as a novel vaccine modality, demonstrating unique advantages including high stability, low innate immunogenicity, and sustained antigen expression. Although early research has predominantly focused on viral targets, accumulating evidence now supports the application potential of circRNA vaccines against diverse pathogens, particularly antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Through encoding critical antigens or virulence factors, these circRNA vaccines demonstrate capability to induce protective immune responses, presenting a viable alternative to conventional antimicrobial strategies. This review highlights recent advances in circRNA vaccine development, spanning synthetic circularization techniques, delivery approaches, and immunological mechanisms. We emphasize their potential against viral, bacterial, fungal, and parasitic infections, while addressing current challenges and future research directions of this emerging platform. Collectively, these insights underscore circRNA's multifaceted versatility and its expanding relevance in next-generation vaccine innovation.
Keywords: RNA delivery; circRNA vaccine; circular RNA; pathogens infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Artificial intelligence-driven circRNA vaccine development: multimodal collaborative optimization and a new paradigm for biomedical applications.Brief Bioinform. 2025 May 1;26(3):bbaf263. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaf263. Brief Bioinform. 2025. PMID: 40483546 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and seroefficacy of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jul;28(34):1-109. doi: 10.3310/YWHA3079. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39046101 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct adaptation and epidemiological success of different genotypes within Salmonella enterica serovar Dublin.Elife. 2025 Jun 25;13:RP102253. doi: 10.7554/eLife.102253. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40560760 Free PMC article.
-
AI-Driven Antimicrobial Peptide Discovery: Mining and Generation.Acc Chem Res. 2025 Jun 17;58(12):1831-1846. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00594. Epub 2025 Jun 3. Acc Chem Res. 2025. PMID: 40459283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing beyond conventional vaccines: The potential of next-generation vaccines in combatting antibiotic-resistant bacteria.Indian J Med Microbiol. 2025 Jun 18;56:100896. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmmb.2025.100896. Online ahead of print. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40541724
References
-
- Lin C.-C., Shen Y.-R., Chang C.-C., Guo X.-Y., Young Y.-Y., Lai T.-Y., Yu I.-S., Lee C.-Y., Chuang T.-H., Tsai H.-Y., et al. Terminal uridyltransferase 7 regulates TLR4-triggered inflammation by controlling Regnase-1 mRNA uridylation and degradation. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:3878. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24177-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- No.82360120, 82460111/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 202205AG070053-04, 2023A4010403-04/Yunnan Provincial Key Laboratory of Clinical Virology
- No.KHBS-2022013, KHYJ-2023-05-01, 2022-KHRCBZ-B03/the The First People's Hospital of Yunnan Province Talent Project program
- No. H-2024064/Yunnan Health training project of high level talents
- 202301AY070001-007/the Kunming Medical University Joint Special Project on Applied Basic Research
- 202301AT070034/Yunnan Foundmental basical research project
- KH-SWR-MY-2019-009, YNWR-MY-2018-020/the Yunnan Province Famous Doctor program
- No.2022ZDKFKT001/the Yunnan Provincial Key Laboratory of Birth Defects and Genetic Diseases
- No.2023YJZX-LN03/13 of 202102AA3100692023/the Open Project of Yunnan Provincial Clinical Medical Research Center for Elderly Diseases
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

