Quality by Design and In Silico Approach in SNEDDS Development: A Comprehensive Formulation Framework
- PMID: 40574014
- PMCID: PMC12195909
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060701
Quality by Design and In Silico Approach in SNEDDS Development: A Comprehensive Formulation Framework
Abstract
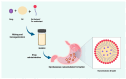
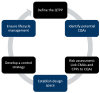
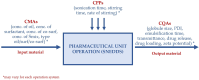
Background/Objectives: The Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System (SNEDDS) has been widely applied in oral drug delivery, particularly for poorly water-soluble compounds. The successful development of SNEDDS largely depends on the precise composition of its components. This narrative review provides an in-depth analysis of Quality by Design (QbD), Design of Experiment (DoE), and in silico approach applications in SNEDDS development. Methods: The review is based on publications from 2020 to 2025, sourced from reputable scientific databases (Pubmed, Science direct, Taylor and francis, and Scopus). Results: Quality by Design (QbD) is a systematic and scientific approach that enhances product quality while ensuring the robustness and reproducibility of SNEDDS, as outlined in the Quality Target Product Profile (QTPP). DoE was integrated into the QbD framework to systematically evaluate the effects of predefined factors, particularly Critical Material Attributes (CMAs) and Critical Process Parameters (CPPS), on the desired responses (Critical Quality Attributes/CQA), ultimately leading to the identification of the optimal SNEDDS formulation. Various DoEs, including the mixture design, response surface methodology, and factorial design, have been widely applied to SNEDDS formulations. The experimental design facilitates the analysis of the relationship between CQA and CMA/CPP, enabling the identification of optimized formulations with enhanced biopharmaceutical, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic profiles. As an essential addition to this review, in silico approach emerges as a valuable tool in the development of SNEDDS, offering deep insights into self-assembly dynamics, molecular interactions, and emulsification behaviour. By integrating molecular simulations with machine learning, this approach enables rational and efficient optimization. Conclusions: The integration of QbD, DoE, and in silico approaches holds significant potential in the development of SNEDDS. These strategies enable a more efficient, rational, and predictive formulation process.
Keywords: SNEDDS; design of experiment; molecular modelling; optimization; quality by design.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Review on QbD-Driven Optimization of Lipid Nanoparticles for Oral Drug Delivery: From Framework to Formulation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 3;20:8611-8651. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S534137. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40626137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accreditation through the eyes of nurse managers: an infinite staircase or a phenomenon that evaporates like water.J Health Organ Manag. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1108/JHOM-01-2025-0029. Online ahead of print. J Health Organ Manag. 2025. PMID: 40574247
-
Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Tucker G., DeSilva B., Dressman J., Ito M., Kumamoto T., Mager D., Mahler H.-C., der Zee A.H.M.-V., Pauletti G.M., Sasaki H., et al. Current Challenges and Potential Opportunities for the Pharmaceutical Sciences to Make Global Impact: An FIP Perspective. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016;105:2489–2497. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2015.12.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gyawali R., Aryal S., Regmi Y., Rajarajan S. Cocrystallization: An Approach to Improve Bioavailability by Altering Physicochemical Properties of Poorly Soluble API’s. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Res. 2021;20:381–397. doi: 10.25166/ijppr.2021.v20i04.28. - DOI
-
- Singh D., Bedi N., Tiwary A.K. Enhancing solubility of poorly aqueous soluble drugs: Critical appraisal of techniques. J. Pharm. Investig. 2018;48:509–526. doi: 10.1007/s40005-017-0357-1. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials