Harnessing Real-Time UV Imaging and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Unlocking New Opportunities for Empirical In Vitro-In Vivo Relationship Modelling
- PMID: 40574041
- PMCID: PMC12196273
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060728
Harnessing Real-Time UV Imaging and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Unlocking New Opportunities for Empirical In Vitro-In Vivo Relationship Modelling
Abstract
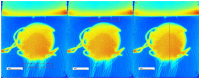
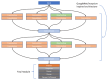
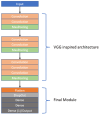
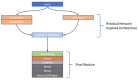
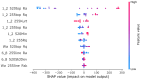
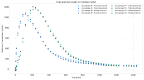
Background: This study delves into the potential use of real-time UV imaging of the dissolution process combined with convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to develop multidimensional models representing the relation between in vitro and in vivo performance of drugs. Method: We utilised the capabilities of the SDi2 apparatus (Pion) to capture multidimensional dissolution data for two distinct Glucophage tablets: immediate-release 500 mg tablets and extended-release 750 mg tablets. The dissolution process was studied in various media, including a compendial pH 1.2 HCl solution, reverse osmosis water, and pH 6.8 phosphate buffer. Result: Moreover, results were captured at different wavelengths (255 nm and 520 nm) to provide a comprehensive view of the process. Our investigation focuses on two primary approaches: (1) analysing numerical data extracted from SDi2 images via a surface characterisation tool, using traditional machine learning techniques, including Scikit-learn, Tensorflow, and AutoML, and (2) utilising raw SDi2 images to train CNNs for direct prediction of in vivo metformin plasma concentrations. Conclusions: This dual approach allows us to assess the impact of data extraction on model performance and explore the potential of CNNs to capture complex dissolution patterns directly from images, potentially revealing hidden information not captured by traditional numerical data extraction methods.
Keywords: SDi2; artificial intelligence (AI); convolutional neural networks (CNN); in vitro in vivo relationship; surface dissolution UV imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shrivas M., Khunt D., Shrivas M., Choudhari M., Rathod R., Misra M. Advances in In Vivo Predictive Dissolution Testing of Solid Oral Formulations: How Closer to In Vivo Performance? J. Pharm. Innov. 2020;15:296–317. doi: 10.1007/s12247-019-09392-6. - DOI
-
- Kostewicz E.S., Abrahamsson B., Brewster M., Brouwers J., Butler J., Carlert S., Dickinson P.A., Dressman J., Holm R., Klein S., et al. In Vitro Models for the Prediction of In Vivo Performance of Oral Dosage Forms. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014;57:342–366. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2013.08.024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Butler J., Hens B., Vertzoni M., Brouwers J., Berben P., Dressman J., Andreas C.J., Schaefer K.J., Mann J., McAllister M., et al. In Vitro Models for the Prediction of in Vivo Performance of Oral Dosage Forms: Recent Progress from Partnership through the IMI OrBiTo Collaboration. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019;136:70–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.12.010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zaborenko N., Shi Z., Corredor C.C., Smith-Goettler B.M., Zhang L., Hermans A., Neu C.M., Alam M.A., Cohen M.J., Lu X., et al. First-Principles and Empirical Approaches to Predicting In Vitro Dissolution for Pharmaceutical Formulation and Process Development and for Product Release Testing. AAPS J. 2019;21:32. doi: 10.1208/s12248-019-0297-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

