Current and Emerging Therapies for Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE): A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 40574065
- PMCID: PMC12196940
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060753
Current and Emerging Therapies for Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE): A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
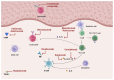
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, immune-mediated disorder that is characterized by symptoms of esophageal dysfunction and the presence of increased eosinophils in the esophageal mucosa. It is becoming increasingly prevalent among children and adults and its pathogenesis arises from the complex interaction of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers, both which contribute to esophageal inflammation. Current societal guidelines recommend the use of proton pump inhibitors, topical steroids, and dietary interventions such as elimination diets as first-line treatments, however, the recent approval of Dupliumab has provided an additional therapeutic avenue. There are a number of investigational biologic agents targeting other immune pathways which are making their way through the pipeline of pharmacologic options in treating this chronic disorder.
Keywords: EGID; EoE; eosinophilic esophagitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lucendo A.J., Molina-Infante J., Arias Á., von Arnim U., Bredenoord A.J., Bussmann C., Amil Dias J., Bove M., González-Cervera J., Larsson H., et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: Evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017;5:335–358. doi: 10.1177/2050640616689525. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dhar A., Haboubi H.N., Attwood S.E., Auth M.K.H., Dunn J.M., Sweis R., Morris D., Epstein J., Novelli M.R., Hunter H., et al. British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) and British Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (BSPGHAN) joint consensus guidelines on the diagnosis and management of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children and adults. Gut. 2022;71:1459–1487. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327326. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources