Unraveling Nature's Pharmacy: Transforming Medicinal Plants into Modern Therapeutic Agents
- PMID: 40574066
- PMCID: PMC12196529
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060754
Unraveling Nature's Pharmacy: Transforming Medicinal Plants into Modern Therapeutic Agents
Abstract
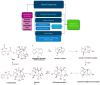
Natural products (NPs) serve as a crucial source for leading bioactive compounds in drug discovery research. Numerous drugs currently utilized as therapeutic agents have been derived from natural origins, with medicinal plant (MP) sources being particularly significant. Despite the advancement of synthetic chemistry, the importance of NPs persists due to their distinct chemical structures and varied biological activities. Moreover, recent advancements in technology have significantly aided in overcoming challenges, primarily due to inherent complexity. This review explores the potential of NPs in the process of drug discovery and development, placing emphasis on the blend of traditional knowledge with modern drug discovery techniques. A brief history of the development of NP drug discovery and examples of significant NPs developed in recent decades are also provided. The focus is on the various methods employed in authentication, selection, extraction/isolation, and bioactivity screening through the application of modern drug-development principles for NPs. Several cutting-edge techniques, such as genetic engineering, metabolic engineering, plant cell culture and synthetic biology utilizing "omics" technologies and computational methodologies enhancing research in NP drug discovery, are also highlighted. There are several problems and inherent challenges regarding NP drug discovery that need to be overcome. Despite the challenges that exist, NPs will be crucial for the future development of new therapeutic drugs, and it is expected that continuous research and the effective utilization of new approaches will further enhance drug discovery efforts.
Keywords: cutting-edge techniques; drug development; drug discovery; medicinal plants; omics technologies; secondary metabolites; traditional medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Surveillance of Barrett's oesophagus: exploring the uncertainty through systematic review, expert workshop and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Mar;10(8):1-142, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta10080. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16545207
-
Psychological interventions for adults who have sexually offended or are at risk of offending.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD007507. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007507.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235646 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sustainable Olive Pomace Extracts for Skin Barrier Support.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jul 25;17(8):962. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17080962. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40870985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ansari M.K.A., Iqbal M., Chaachouay N., Ansari A.A., Owens G. Plants as Medicine and Aromatics. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2023. The Concept and Status of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants: History, Pharmacognosy, Ecology, and Conservation.
-
- Saad B. Greco-Arab and Islamic Herbal Medicine: A Review. Eur. J. Med. Plants. 2014;4:249–258. doi: 10.9734/EJMP/2014/6530. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

