Intranasal Drug Delivery Technology in the Treatment of Central Nervous System Diseases: Challenges, Advances, and Future Research Directions
- PMID: 40574087
- PMCID: PMC12197310
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060775
Intranasal Drug Delivery Technology in the Treatment of Central Nervous System Diseases: Challenges, Advances, and Future Research Directions
Abstract
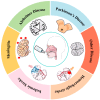
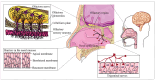
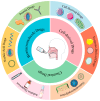
As population aging becomes an increasingly critical global issue, the incidence of central nervous system (CNS) diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), and stroke, has risen sharply. However, the blood-brain barrier (BBB) presents a significant obstacle to the effective treatment of these CNS disorders, limiting the ability of therapeutic agents to reach the brain. In this context, intranasal drug delivery, which bypasses the BBB, has attracted considerable attention in recent years. By utilizing pathways such as the olfactory and trigeminal nerves, intranasal drug delivery facilitates the rapid transport of drugs to the brain, thereby enhancing both the bioavailability and targeting efficiency of the drugs. This review provides an overview of the molecular mechanisms underlying intranasal drug delivery, its advancements in the treatment of CNS diseases, strategies to improve delivery efficiency, and a discussion of the challenges and potential future directions in this field. The aim of this paper is to offer valuable insights and guidance for researchers and clinicians working in the area of CNS disease treatment.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; blood–brain barrier; central nervous system; hydrogels; intranasal drug delivery; nanotechnology; olfactory nerve pathway; small molecules; trigeminal nerve pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

