Revolutionizing Diabetes Management Through Nanotechnology-Driven Smart Systems
- PMID: 40574088
- PMCID: PMC12196884
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060777
Revolutionizing Diabetes Management Through Nanotechnology-Driven Smart Systems
Abstract
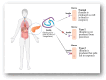
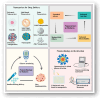
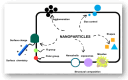
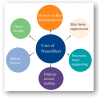
Diabetes is a global health challenge, and while current treatments offer relief, they often fall short in achieving optimal control and long-term outcomes. Nanotechnology offers a groundbreaking approach to diabetes management by leveraging materials at the nanoscale to improve drug delivery, glucose monitoring, and therapeutic precision. Early advancements focused on enhancing insulin delivery through smart nanosystems such as tiny capsules that gradually release insulin, helping prevent dangerous drops in blood sugar. Simultaneously, the development of nanosensors has revolutionised glucose monitoring, offering real-time, continuous data that empowers individuals to manage their condition more effectively. Beyond insulin delivery and monitoring, nanotechnology enables targeted drug delivery systems that allow therapeutic agents to reach specific tissues, boosting efficacy while minimising side effects. Tools like microneedles, carbon nanomaterials, and quantum dots have made treatment less invasive and more patient-friendly. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with nanotechnology marks a new frontier in personalised care. AI algorithms can analyse individual patient data to adjust insulin doses and predict glucose fluctuations, paving the way for more responsive, customised treatment plans. As these technologies advance, safety remains a key concern. Rigorous research is underway to ensure the biocompatibility and long-term safety of these novel materials. The future of diabetes care lies in the convergence of nanotechnology and AI, offering personalised, data-driven strategies that address the limitations of conventional approaches. This review explores current progress, persistent challenges, and the transformative potential of nanotechnology in reshaping diabetes diagnosis and treatment and improving patient quality of life.
Keywords: AI in diabetes management; carbon nanomaterials; continuous glucose monitoring (CGM); diabetes mellitus; diabetic wound healing; drug delivery systems; electrochemical biosensors; glucose biosensors; glucose monitoring; insulin delivery; microneedles; nanofibers; nanomedicine; nanotechnology; non-invasive monitoring; polymeric nanoparticles; quantum dots (QDs); smart nanocarriers; wearable biosensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Methods for insulin delivery and glucose monitoring in diabetes: summary of a comparative effectiveness review.J Manag Care Pharm. 2012 Aug;18(6 Suppl):S1-17. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2012.18.s6-a.1. J Manag Care Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22984955 Free PMC article.
-
Accreditation through the eyes of nurse managers: an infinite staircase or a phenomenon that evaporates like water.J Health Organ Manag. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1108/JHOM-01-2025-0029. Online ahead of print. J Health Organ Manag. 2025. PMID: 40574247
-
Integrated sensor-augmented pump therapy systems [the MiniMed® Paradigm™ Veo system and the Vibe™ and G4® PLATINUM CGM (continuous glucose monitoring) system] for managing blood glucose levels in type 1 diabetes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2016 Feb;20(17):v-xxxi, 1-251. doi: 10.3310/hta20170. Health Technol Assess. 2016. PMID: 26933827 Free PMC article.
-
Smart nanoparticles for responsive drug delivery in Diabetes: Advances, Challenges, and future Perspectives.Int J Pharm. 2025 Aug 20;681:125817. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125817. Epub 2025 Jun 6. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40484155 Review.
-
Nano-based therapy for type 1 diabetes: from immuno-intervention to insulin delivery.Acta Biomater. 2025 Jul 1;201:101-120. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2025.06.016. Epub 2025 Jun 20. Acta Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40544026 Review.
References
-
- Mukhtar Y., Galalain A., Yunusa U. A Modern Overview on Diabetes Mellitus: A Chronic Endocrine Disorder. Eur. J. Biol. 2020;5:1–14. doi: 10.47672/ejb.409. - DOI
-
- Alam S., Hasan M.K., Neaz S., Hussain N., Hossain M.F., Rahman T. Diabetes Mellitus: Insights from Epidemiology, Biochemistry, Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Complications and Comprehensive Management. Diabetology. 2021;2:36–50. doi: 10.3390/diabetology2020004. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

