Liposomal Encapsulation of Carob (Ceratonia siliqua L.) Pulp Extract: Design, Characterization, and Controlled Release Assessment
- PMID: 40574089
- PMCID: PMC12196410
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060776
Liposomal Encapsulation of Carob (Ceratonia siliqua L.) Pulp Extract: Design, Characterization, and Controlled Release Assessment
Abstract
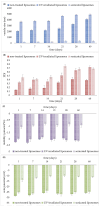
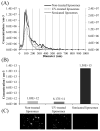
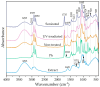
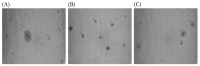
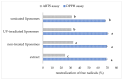
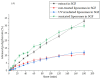
Background: Carob (Ceratonia siliqua L.) pulp flour is primarily used in the food industry. As a rich source of bioactive compounds, particularly polyphenols, it holds promise for pharmaceutical formulation research and development. Objectives: This study focused on developing liposomal particles loaded with carob pulp extract using the proliposome method, followed by modifications through UV irradiation and sonication. Methods: The resulting liposomes were analyzed for encapsulation efficiency, vesicle size, polydispersity index (PDI), mobility, zeta potential, viscosity, surface tension, density, antioxidant activity, FT-IR spectra, and release kinetics under simulated gastrointestinal conditions. In addition, nanoparticle tracking analysis and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were used for liposomal characterization. Results: The findings revealed a high encapsulation efficiency across all samples (>70%). The particle size and PDI measurements confirmed the presence of a multilamellar and uniform liposomal system before post-processing modifications. The medium value of zeta potential suggested a moderately electrostatically stabilized liposomal suspension. The sonicated liposomes demonstrated a higher concentration of vesicles in comparison to non-treated and UV-irradiated samples. TEM analysis revealed purified liposomal vesicles with preserved structural integrity. Encapsulation, as well as UV irradiation and sonication of liposomes, did not diminish the extract's anti-DPPH activity. However, the ABTS radical scavenging potential of the pure extract was significantly lower compared to its encapsulated counterparts. UV irradiation and sonication notably reduced the anti-ABTS capacity of the extract-liposome system. Monitoring the release of bioactive compounds demonstrated controlled delivery from liposomal particles under simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Conclusions: Overall, liposomal formulations of carob pulp extract exhibit significant potential for further development as a functional food ingredient or for use in the prevention and treatment of various diseases.
Keywords: antioxidant activity; carob pulp extract; controlled release; encapsulation efficiency; liposomal formulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dahmani W., Elaouni N., Abousalim A., Akissi Z.L.E., Legssyer A., Ziyyat A., Sahpaz S. Exploring Carob (Ceratonia siliqua L.): A Comprehensive Assessment of Its Characteristics, Ethnomedicinal Uses, Phytochemical Aspects, and Pharmacological Activities. Plants. 2023;12:3303. doi: 10.3390/plants12183303. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zahorec J., Šoronja-Simović D., Kocić-Tanackov S., Bulut S., Martić N., Bijelić K., Božović D., Pavlić B. Carob Pulp Flour Extract Obtained by a Microwave-Assisted Extraction Technique: A Prospective Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Agent. Separations. 2023;10:465. doi: 10.3390/separations10090465. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 451-03-136/2025-03/200019/Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation, Republic of Serbia
- 451-03-136/2025-03/200026/Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation, Republic of Serbia
- Project No. 003070282 2024 09418 003 000 000 001/Provincial Secretariat for Higher Education and Scientific Research of Vojvodina
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

