Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose-A Key Excipient in Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Systems
- PMID: 40574096
- PMCID: PMC12196896
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060784
Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose-A Key Excipient in Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Systems
Abstract
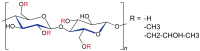
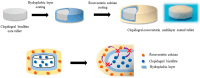
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (Hypromellose, HPMC) is a well-known excipient used in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical fields due to its versatile physicochemical properties. HPMC (derived from cellulose and obtained through etherification) varies in polymerization degree and viscosity, factors that both influence its functional applications. Usually, an increased polymerization degree implies a higher viscosity, depending also on the amount of polymer used. Hypromellose plays a crucial role in solid dosage forms, serving as a binder in the case of controlled-release tablets, a film-forming agent in the case of orodispersible films and mucoadhesive films, and a release modifier due to its presence in different polymerization degrees in the case of extended or modified release tablets. However, its compatibility with other excipients and the active ingredient must be carefully evaluated to prevent formulation challenges via several analytical methods such as differential scanned calorimetry (DSC), Fourier Transformed Infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-Ray Particle Diffraction (XRPD), and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). This review explores the physicochemical characteristics, and diverse applications of HPMC, emphasizing its significance in modern drug delivery systems.
Keywords: binder; film-forming agent; hydroxypropyl methylcellulose; polymerization degree; viscosity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advancements in hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-polyethylene glycol hybrid excipients and their nanoformulations for controlled and ligand-directed biologic delivery.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 19. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04449-5. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40682687 Review.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Nebuliser systems for drug delivery in cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 9;11(11):CD007639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007639.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37942828 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(3):CD000213. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000213. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Oct 07;(4):CD000213. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000213.pub2. PMID: 12917889 Updated.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seddiqi H., Oliaei E., Honarkar H., Jin J., Geonzon L.C., Bacabac R.G., Klein-Nulend J. Cellulose and Its Derivatives: Towards Biomedical Applications. Cellulose. 2021;28:1893–1931. doi: 10.1007/s10570-020-03674-w. - DOI
-
- Timmins P., Pygall S.R., Melia C.D. Hydrophilic Matrix Dosage Forms: Definitions, General Attributes, and the Evolution of Clinical Utilization. In: Timmins P., Pygall S.R., Melia C.D., editors. Hydrophilic Matrix Tablets for Oral Controlled Release. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2014. pp. 1–15.
-
- Yu X., Liu Q., Jin Z., Jiao A. Preparation and Characterization of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose/Hydroxypropyl Starch Composite Films Reinforced by Chitosan Nanoparticles of Different Sizes. Mater. Today Commun. 2023;35:105714. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.105714. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources