Enhancing Resident Note Documentation: A Quality Improvement Initiative to Accurately Capture Patient Complexity
- PMID: 40574737
- PMCID: PMC12197967
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajmo.2025.100104
Enhancing Resident Note Documentation: A Quality Improvement Initiative to Accurately Capture Patient Complexity
Abstract
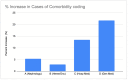
Provider notes serve as a critical component of physician workflow, documenting essential aspects of patient care while also fulfilling regulatory and billing requirements. With increasing documentation complexity introduced by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and the 2021 mandate for open access to clinical notes, physicians in training must develop skills to accurately document patient complexity. This quality improvement initiative aimed to enhance inpatient note documentation by internal medicine residents, focusing on improving the capture of medical complexity in coding and billing standards. Our intervention included the development and implementation of a standardized progress note template, a structured scoring rubric, multidisciplinary rounds and curriculum integrating faculty and peer-led feedback. The study measured documentation improvements through rubric scores, Length of Stay Index (LOSi), and complications or comorbidities (CC) and major complications or comorbidities (MCC) capture rates. Results demonstrated improvements in LOSi and enhanced CC/MCC capture, leading to improved institutional performance metrics. This initiative highlights the necessity of integrating formal note-writing training within residency curricula to meet evolving documentation demands.
Keywords: Clinical documentation; Medical education; Quality metrics.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accreditation through the eyes of nurse managers: an infinite staircase or a phenomenon that evaporates like water.J Health Organ Manag. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1108/JHOM-01-2025-0029. Online ahead of print. J Health Organ Manag. 2025. PMID: 40574247
-
Faculty development initiatives designed to promote leadership in medical education. A BEME systematic review: BEME Guide No. 19.Med Teach. 2012;34(6):483-503. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2012.680937. Med Teach. 2012. PMID: 22578043
-
Patient-doctor communication.Med Clin North Am. 2003 Sep;87(5):1115-45. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(03)00066-x. Med Clin North Am. 2003. PMID: 14621334
-
The educational effects of portfolios on undergraduate student learning: a Best Evidence Medical Education (BEME) systematic review. BEME Guide No. 11.Med Teach. 2009 Apr;31(4):282-98. doi: 10.1080/01421590902889897. Med Teach. 2009. PMID: 19404891
-
A systematic review of faculty development initiatives designed to improve teaching effectiveness in medical education: BEME Guide No. 8.Med Teach. 2006 Sep;28(6):497-526. doi: 10.1080/01421590600902976. Med Teach. 2006. PMID: 17074699
References
-
- A Look into the History and Evolution of Medical Documentation | CKEditor | CKEditor. Accessed September 12, 2024. https://ckeditor.com/blog/history-of-medical-documentation/.
-
- WANT W. Documentation guidelines for evaluation and management services. online. 1995 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources