Antidepressant and neuromodulatory potential of hydroalcoholic extract of Helianthus annuus florets in mouse models of depression
- PMID: 40574754
- PMCID: PMC12198942
- DOI: 10.1515/tnsci-2025-0376
Antidepressant and neuromodulatory potential of hydroalcoholic extract of Helianthus annuus florets in mouse models of depression
Abstract
Background: Depression is a pervasive neuropsychiatric disorder having significant social and economic impacts and often linked to imbalances in neurotransmitter systems. Traditional herbal medicines have garnered attention for their potential antidepressant effects, with limited research on Helianthus annuus (sunflower) as a therapeutic option.
Objectives: The present study was carried out to investigate the anti-depressant and neuromodulatory potential of hydroalcoholic extract of Helianthus annuus (H. annuus) florets in mouse models of depression.
Methods: Depression was induced in rats by the forced swim test (FST) and tail suspension test (TST). The hydroalcoholic extract of H. annuus was used as the test drug given in the doses of 200 and 400 mg/kg, whereas fluoxetine was used as the standard drug.
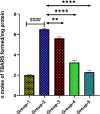
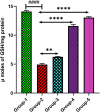
Results: The results revealed that the H. annuus extract decreased the immobility time significantly as reflected in FST and TST. Treatment with H. annuus extract also demonstrated significant improvement in the swimming and climbing times as reflected in FST. Administration of H. annuus extract significantly improved neurotransmitter levels such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which were significantly lowered in depression control rats. The mean value of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances was significantly lowered after the administration of H. annuus extract. Additionally, the levels of glutathione, superoxide dismutase, and catalase were significantly increased after the administration of H. annuus extract. Additionally, the mean value of inflammatory cytokines, for example, tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 were reduced significantly in groups treated with H. annuus extract.
Conclusions: The results suggest that H. annuus extract exhibited significant antidepressant and neuromodulatory potential by ameliorating behavioural parameters, oxidative stress, and inflammatory markers.
Keywords: Helianthus annuus; brain monoamines; depression; inflammatory markers; oxidative stress.
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: All authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
