From Biased Selective Labels to Pseudo-Labels: An Expectation-Maximization Framework for Learning from Biased Decisions
- PMID: 40574796
- PMCID: PMC12199211
From Biased Selective Labels to Pseudo-Labels: An Expectation-Maximization Framework for Learning from Biased Decisions
Abstract
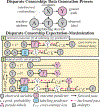
Selective labels occur when label observations are subject to a decision-making process; e.g., diagnoses that depend on the administration of laboratory tests. We study a clinically-inspired selective label problem called disparate censorship, where labeling biases vary across subgroups and unlabeled individuals are imputed as "negative" (i.e., no diagnostic test = no illness). Machine learning models naïvely trained on such labels could amplify labeling bias. Inspired by causal models of selective labels, we propose Disparate Censorship Expectation-Maximization (DCEM), an algorithm for learning in the presence of disparate censorship. We theoretically analyze how DCEM mitigates the effects of disparate censorship on model performance. We validate DCEM on synthetic data, showing that it improves bias mitigation (area between ROC curves) without sacrificing discriminative performance (AUC) compared to baselines. We achieve similar results in a sepsis classification task using clinical data.
Figures
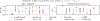
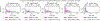
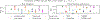
References
-
- Adams R, Henry KE, Sridharan A, Soleimani H, Zhan A, Rawat N, Johnson L, Hager DN, Cosgrove SE, Markowski A, et al. Prospective, multi-site study of patient outcomes after implementation of the trews machine learning-based early warning system for sepsis. Nature Medicine, pp. 1–6, 2022. - PubMed
-
- Ambroise C and Govaert G EM algorithm for partially known labels. In Data Analysis, Classification, and Related Methods, pp. 161–166. Springer, 2000.
-
- Arazo E, Ortego D, Albert P, O’Connor NE, and McGuinness K Pseudo-labeling and confirmation bias in deep semi-supervised learning. In 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–8. IEEE, 2020.
-
- Arpit D, Jastrzebski S, Ballas N, Krueger D, Bengio E, Kanwal MS, Maharaj T, Fischer A, Courville A, Bengio Y, and Lacoste-Julien S A closer look at memorization in deep networks. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, volume 70 of Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pp. 233–242, 2017.
-
- Bahadori MT, Chalupka K, Choi E, Chen R, Stewart WF, and Sun J Causal regularization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.02604, 2017.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
