Pluripotency genes of mammals: a network at work
- PMID: 40574823
- PMCID: PMC12198222
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1578499
Pluripotency genes of mammals: a network at work
Abstract
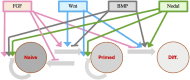
Pluripotency, i.e., the ability to differentiate into cells of all three germ layers, is a transient state of early embryonic cells. In mammals, during progression from pre-implantation to post-implantation stage, pluripotent cells undergo different state transitions characterized by changes in gene expression and development potential. These developmental states include: (i) a naive pluripotency (pre-implantation embryonic stem cells, or ESCs), (ii) an intermediate condition (formative state), and (iii) a primed pluripotency (late post-implantation ESCs derived from epiblasts also named EpiSCs). The transitions are regulated by an interconnected network of pluripotency-related genes. Transcription of genes such as Oct4, Sox2, and Nanog is crucial for obtaining and maintaining pluripotency. These three factors form an autoregulatory loop by binding to each other's promoters to activate their transcription. Other factors play a significant ancillary role in the transcription factor network preserving cell pluripotency. In the review, we will also mention some of the more relevant cytokines, molecules, signaling pathways, and epigenetic modifications that induce and control pluripotency gene expression. The main goal of this review is to bridge the gap between the fields of genetics and stem cell biology and to set the ground for the application of this knowledge to the development of strategies and drugs to be used in a clinical environment.
Keywords: Nanog; Oct4; Sox2; pluripotency genes; pluripotent cells; stem cells.
Copyright © 2025 Cancedda and Mastrogiacomo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
The educational effects of portfolios on undergraduate student learning: a Best Evidence Medical Education (BEME) systematic review. BEME Guide No. 11.Med Teach. 2009 Apr;31(4):282-98. doi: 10.1080/01421590902889897. Med Teach. 2009. PMID: 19404891
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

