Recombinant humanized collagen combined with nicotinamide increases the expression level of rat basement membrane proteins and promotes hair growth
- PMID: 40574828
- PMCID: PMC12198190
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1546779
Recombinant humanized collagen combined with nicotinamide increases the expression level of rat basement membrane proteins and promotes hair growth
Abstract
Background: Hair follicle stem cells (HFSCs) play crucial roles in hair growth and are expected to be potential targets in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
Method: This study aims to investigate the positive effect on hair growth by the recombinant human collagen complex (RHC complex), composed of rhCOL III, rhCOL XVII, and rhCOL XXI, along with nicotinamide, both in vitro and in vivo, by HFSCs and rat models. The survival rate, function, and differentiation of HFSCs were investigated.
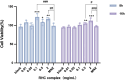
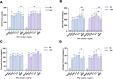
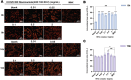
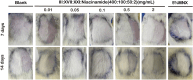
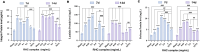
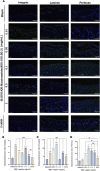
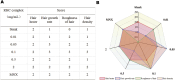
Results: The CCK-8 experiment showed that the RHC complex was non-toxic to HFSCs, and the cell survival rate exceeded 80% after 8 and 16 h of treatment. The ELISA method showed that the RHC complex significantly increased the intracellular vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels. In addition, the increase in the content of trichohyalin (a key structural protein of hair) indicates that the structure and function of hair follicles may be enhanced. The expression levels of β-integrin and p63 were significantly upregulated, which are crucial for cell adhesion, migration, and maintenance of HFSCs homeostasis. In the rat model, significant hair growth was observed after a 7-day treatment period. The period of vigorous hair growth in rats was selected for immunofluorescence, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining analysis. The results showed that the RHC complex could promote the expression of Integrin, Laminin and Perlecan, which were conducive to maintaining the stability of the microenvironment of HFSCs. Additionally it facilitated the migration and differentiation of HFSCs, as evidenced by an increased number of hair follicles in HE-stained skin tissues. In conclusion, the RHC complex exhibited high HFSCs survival rates and enhanced the expression of HFSCs-associated factors and basement membrane proteins. These properties make the RHC complex a promising novel ingredient for promoting hair growth, preventing hair loss, and maintaining hair health.
Keywords: VEGF; hair follicle stem cells; hair loss; recombinant humanized collagen; trichohyalin.
Copyright © 2025 Zhou, Chen, Ye, Sun, Wang, Diao and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
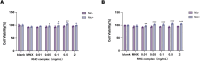

Similar articles
-
Lnc056 Enhances Hair Follicle Stem Cells Proliferation by Binding Transcription Factor HNRNPUL1 to Up-Regulate TRIP6 Expression.FASEB J. 2025 Jun 30;39(12):e70764. doi: 10.1096/fj.202500381R. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40552937
-
Levetiracetam add-on for drug-resistant focal epilepsy: an updated Cochrane Review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;2012(9):CD001901. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001901.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22972056 Free PMC article.
-
L-borneol regulates rno-miR-127/ PODXL2 to promote hair follicle stem cells to repair skin wounds.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Jun 17;158:114847. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114847. Epub 2025 May 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40378434
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Inhaled mannitol for cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 9;2(2):CD008649. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008649.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 1;5:CD008649. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008649.pub4. PMID: 29424930 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Brennan M., Bhatti H., Nerusu K. C., Bhagavathula N., Kang S., Fisher G. J., et al. (2003). Matrix metalloproteinase‐1 is the major collagenolytic enzyme responsible for collagen damage in UV‐irradiated human skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 78 (1), 43. 10.1562/0031-8655(2003)078<0043:mmitmc>2.0.co; - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

