Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- PMID: 40574908
- PMCID: PMC12198945
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2025-1219
Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of the study was to examine peripheral oxygen saturation values in the index and middle fingers of the dominant hand in healthy young adults measured while lying in a supine position or sitting straight up.
Methods: This study was a non-randomized and non-controlled, quasi-experimental repeated measures study. It was conducted with 200 healthy young adults in Turkey. A pulse oximeter was located at the same time on the index and middle fingers of the active hand of each participant while sitting upright, and after being kept there for 1 min, the results of the measurements were recorded. Later, the participants were brought into a supine position, and after 10 min of rest, measurements with a pulse oximeter placed on the index and middle fingers of the active hand were repeated in the same way.
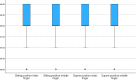
Results: The mean age of the participants was 20.4 ± 1.8 years; 76.5% were female, and their mean body mass index was 22.5 ± 3.6 kg/m2. It was found that when the individuals were sitting upright, the peripheral oxygen saturation values measured from the middle finger were significantly higher than the peripheral oxygen saturation values measured from the middle finger in the supine position (p = 0.003). It was found that the peripheral oxygen saturation values of female participants measured from the index finger in the upright sitting position and from the index and middle fingers in the supine position were significantly higher than the saturation values of male participants (p = 0.018, p < 0.001, p = 0.001, respectively). In addition, it was found that the peripheral oxygen saturation values measured from the index and middle fingers of underweight individuals in the sitting position and from the index and middle fingers in the supine position were significantly higher than the saturation values of overweight individuals (p = 0.021, p = 0.006, p = 0.001, respectively).
Conclusion: In the conclusions of this study, it was found that the highest oxygen saturation value of the young adults was measured from the middle finger when they were in the upright sitting position. It was also found that the variables of gender and body mass index significantly affected the peripheral oxygen saturation value.
Keywords: body positions; healthy individuals; oxygenation; peripheral oxygen saturation; pulse oximeter.
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest or any competing interests regarding the results and/or discussions reported in this research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Positioning for acute respiratory distress in hospitalised infants and children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 6;6(6):CD003645. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003645.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35661343 Free PMC article.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Infant position in neonates receiving mechanical ventilation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 7;11(11):CD003668. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003668.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27819747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khan A, Khan B, Jameel A. Comparison of oxygen saturation in different fingers of hands measured by portable pulse oximeter in healthy adults. Med Forum. 2023;34(9):20–3.
-
- Elliott M, Williamson R. Do nursing textbooks accurately describe pulse oximetry? An audit of current literature. Br J Nurs. 2020;29(11):594–600. - PubMed
-
- Tor Ö, Mert G, Tosun B. Effects of positions on hemodynamic parameters of patients in intensive care unit. J Dokuz Eylul Univ Nurs Fac. 2019;12(1):15–20.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources