Temporary bilateral uterine artery occlusion in the control of hemorrhage: A case report and review of literature
- PMID: 40574923
- PMCID: PMC11926927
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i18.101309
Temporary bilateral uterine artery occlusion in the control of hemorrhage: A case report and review of literature
Abstract
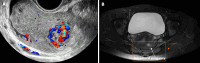
Background: Intramural pregnancy is rare, with an unclear etiology and pathophysiology. Surgical, medical, and expectant management options are available for this condition. However, most reported cases are managed surgically. Despite the risks of massive intraoperative bleeding and acute and long-term complications, uterine artery embolization is often selected. Temporary occlusion of the bilateral uterine arteries during surgery is associated with fewer complications.
Case summary: We reported the case of a patient who was diagnosed with intramural pregnancy approximately one month after medical abortion. We performed laparoscopic resection with hysteroscopy. Since the lesion had abundant blood flow, we temporarily blocked the bilateral uterine arteries to prevent massive intraoperative bleeding. The surgical process went smoothly. The postoperative course was uneventful.
Conclusion: Temporary occlusion of the bilateral uterine arteries in the treatment of intramural pregnancy may prevent excessive uterine bleeding during surgery.
Keywords: Case report; Hysteroscopy; Intramural pregnancy; Laparoscopic surgery; Uterine artery temporary occlusion.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Methods for managing miscarriage: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jun 1;6(6):CD012602. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012602.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34061352 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative medical therapy before surgery for uterine fibroids.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 15;11(11):CD000547. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000547.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Apr 04;4:CD000547. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000547.pub3. PMID: 29139105 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Uterine distension media for outpatient hysteroscopy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Nov 26;11(11):CD006604. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006604.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34826139 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-operative endometrial thinning agents before endometrial destruction for heavy menstrual bleeding.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(3):CD001124. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001124. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jul 29;(7):CD001124. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001124.pub2. PMID: 12137619 Updated.
-
Induction of labour for improving birth outcomes for women at or beyond term.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 9;5(5):CD004945. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004945.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 15;7:CD004945. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004945.pub5. PMID: 29741208 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Ko HS, Lee Y, Lee HJ, Park IY, Chung DY, Kim SP, Park TC, Shin JC. Sonographic and MR findings in 2 cases of intramural pregnancy treated conservatively. J Clin Ultrasound. 2006;34:356–360. - PubMed
-
- Ginsburg KA, Quereshi F, Thomas M, Snowman B. Intramural ectopic pregnancy implanting in adenomyosis. Fertil Steril. 1989;51:354–356. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

