IBS May Have a Causal Effect on Increased Tryptophan Metabolites Levels: Insights from a Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
- PMID: 40575111
- PMCID: PMC12198586
- DOI: 10.1177/11786469251327399
IBS May Have a Causal Effect on Increased Tryptophan Metabolites Levels: Insights from a Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
Background: Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a chronic functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by abdominal pain and altered bowel habits. Tryptophan, an essential amino acid derived from dietary proteins, can be metabolized into various compounds by the gut microbiome. Emerging evidence suggests that tryptophan metabolites play a role in functional gastrointestinal disorders. However, the causal relationship between tryptophan metabolites and IBS remains to be fully elucidated.
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the potential causal relationship between tryptophan metabolites and IBS using Mendelian randomization (MR).
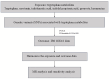
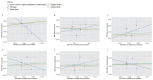
Methods: Instrumental variables (IVs) were selected from summary data of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) for tryptophan and IBS. SNPs potentially influencing MR results were excluded through outlier detection using MR-PRESSO. Bidirectional two-sample MR analyses were conducted using the inverse-variance weighted (IVW), MR-Egger regression, weighted median, weighted mode, and simple mode methods. The MR-Egger intercept test was employed to assess pleiotropy and heterogeneity among IVs, with visualization of the MR results through scatter plots, funnel plots, and forest plots.
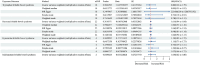
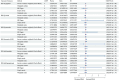
Results: Genetically predicted tryptophan metabolites were not associated with the risk of IBS. In the reverse direction, genetically predicted IBS was associated with increased levels of tryptophan, serotonin, and kynurenine in the IVW analysis. Sensitivity and replication analyses confirmed these findings.
Conclusion: The findings of this Mendelian randomization study suggest that IBS may lead to elevated levels of tryptophan, serotonin, and kynurenine. These results have important implications for understanding the interplay between tryptophan metabolism and IBS in clinical settings. Further research is warranted to explore the underlying mechanisms.
Keywords: Irritable bowel syndrome; Mendelian randomization; causal relationship; kynurenine; tryptophan metabolites.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Bonetto S, Fagoonee S, Battaglia E, Grassini M, Saracco GM, Pellicano R. Recent advances in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Pol Arch Intern Med. 2021;131:709-715. - PubMed
-
- Dinan TG, Cryan JF. The microbiome-gut-brain axis in health and disease. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. 2017;46:77-89. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

