Advancements and Prospects in DNA-Based Bioanalytical Technology for Environmental Toxicant Detection
- PMID: 40575295
- PMCID: PMC12188486
- DOI: 10.1021/jacsau.5c00398
Advancements and Prospects in DNA-Based Bioanalytical Technology for Environmental Toxicant Detection
Abstract
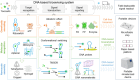
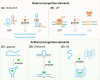
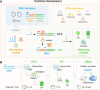
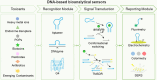
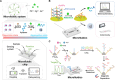
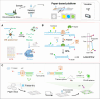
The mounting global crisis of environmental pollution necessitates transformative advances in analytical technologies that combine speed, precision, and field applicability. To meet this demand, next-generation analytical platforms must achieve seamless integration of two critical features: molecular-level recognition fidelity and reliable signal transduction. DNA nanotechnology leverages sequence-specific molecular recognition and programmable self-assembly to enable both natural (e.g., riboswitches) and synthetic (e.g., aptamers, DNAzymes) biosensing modalities. The structural programmability and predictable Watson-Crick base pairing of DNA provide a modular framework for designing next-generation biosensors with tunable specificity and sensitivity. When integrated with portable point-of-care (POC) platforms, these biosensing systems enable field-deployable, rapid, and operator-agnostic detection of toxicants across diverse matrixes, making them highly suitable for complex environmental monitoring tasks. This perspective highlights the potential and strategic approaches for constructing biosensors utilizing DNA-based recognition elements and structural materials. It explores the progress in field-deployable DNA-based biosensors, which are revolutionizing the on-site detection of environmental toxicants. We also discuss the current challenges and future perspectives for DNA-based biosensing systems in environmental pollution monitoring, offering insights into their broader applications.
Keywords: DNA-based biosensing system; Recognition element; cell-free biosensor; environmental monitoring; field deployment.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Advances in Breast Cancer Detection: Biomarkers, Mechanisms, and Biosensor Technologies.Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2025 Jun 27:1-32. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2025.2521431. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40576081 Review.
-
Diagnostic test accuracy and cost-effectiveness of tests for codeletion of chromosomal arms 1p and 19q in people with glioma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 2;3(3):CD013387. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013387.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35233774 Free PMC article.
-
Accreditation through the eyes of nurse managers: an infinite staircase or a phenomenon that evaporates like water.J Health Organ Manag. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1108/JHOM-01-2025-0029. Online ahead of print. J Health Organ Manag. 2025. PMID: 40574247
-
Perceptions and experiences of the prevention, detection, and management of postpartum haemorrhage: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 27;11(11):CD013795. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013795.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 38009552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tijani J. O., Fatoba O. O., Babajide O. O., Petrik L. F.. Pharmaceuticals, Endocrine Disruptors, Personal Care Products, Nanomaterials and Perfluorinated Pollutants: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016;14(1):27–49. doi: 10.1007/s10311-015-0537-z. - DOI
-
- Jiang G.. Preface to the Special Topic on Environmental Pollution and Health Risk. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2016;3(4):409–409. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nww090. - DOI
-
- Waqas W., Yuan Y., Ali S., Zhang M., Shafiq M., Ali W., Chen Y., Xiang Z., Chen R., Ikhwanuddin M., Ma H.. Toxic Effects of Heavy Metals on Crustaceans and Associated Health Risks in Humans: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024;22(3):1391–1411. doi: 10.1007/s10311-024-01717-3. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
