Selective CBP/EP300 Bromodomain Inhibitors: Novel Epigenetic Tools to Counter TNF-α-Driven Inflammation
- PMID: 40575322
- PMCID: PMC12188386
- DOI: 10.1021/jacsau.5c00085
Selective CBP/EP300 Bromodomain Inhibitors: Novel Epigenetic Tools to Counter TNF-α-Driven Inflammation
Abstract
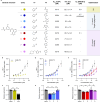
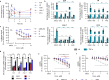
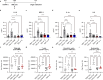
Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) is a central driver of inflammation in autoimmune conditions such as Crohn's disease and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Targeting epigenetic regulators involved in cytokine expression holds therapeutic promise, yet the precise role of the CBP/EP300 bromodomains (BRDs) in modulating immune responses remains poorly understood. Here, we introduce a distinct class of selective CBP/EP300-BRD inhibitors based on a unique 3-methylcinnoline acetyl-lysine mimic, identified through high-throughput fragment docking. These inhibitors significantly reduce TNF-α-driven cytokine expression in vitro by blocking NFκB signaling in immune cells. In vivo, BRD inhibition led to a robust anti-inflammatory effect, decreasing cytokine secretion (including IL-1β, MCP-1, IL-1α, and IL-6) and preventing immune cell migration to inflamed lymph nodes in a TNF-α-stimulated murine model. Our findings highlight CBP/EP300-BRDs as promising targets for autoimmune therapy, with these non-cytotoxic inhibitors offering a potential complementary approach for RA and other TNF-α-mediated inflammatory conditions.
Keywords: CBP/EP300; NFκB; TNF-α; bromodomain inhibitors; epigenetics; inflammation.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures
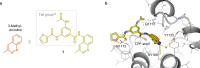
References
-
- Furman D., Campisi J., Verdin E., Carrera-Bastos P., Targ S., Franceschi C., Ferrucci L., Gilroy D. W., Fasano A., Miller G. W., Miller A. H., Mantovani A., Weyand C. M., Barzilai N., Goronzy J. J., Rando T. A., Effros R. B., Lucia A., Kleinstreuer N., Slavich G. M.. Chronic Inflammation in the Etiology of Disease across the Life Span. Nat. Med. 2019;25(12):1822–1832. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0675-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
