Phase II study of axitinib in patients with NF2-related schwannomatosis and progressive vestibular schwannomas
- PMID: 40575410
- PMCID: PMC12199335
- DOI: 10.1093/noajnl/vdaf083
Phase II study of axitinib in patients with NF2-related schwannomatosis and progressive vestibular schwannomas
Abstract
Background: Axitinib is an oral multi-receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), and c-KIT. These represent a clinically and/or preclinically validated molecular targets in vestibular schwannoma (VS).
Methods: Eligible patients were age > 5 years with a clinical diagnosis of NF2-related schwannomatosis (NF2-SWN) and at least one volumetrically measurable, progressive VS. Axitinib was given continuously in 28-day cycles for up to of 12 cycles. Primary endpoint was objective volumetric response rate to axitinib, hearing response was a secondary endpoint, along with validated quality of life assessments (NFTI-QOL).
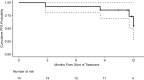
Results: Twelve patients were enrolled and 8 completed 12 cycles, including 2 pediatric patients. Ten patients were evaluated for the primary endpoint, defined as ≥ 20% decrease in VS volume, with 2 volumetric responses observed; both were reached after 3 cycles and sustained during treatment. The best volumetric response was -53.9% after 9 cycles. Three hearing responses were observed, one of which was sustained during treatment. All patients experienced drug-related toxicities, the most common were diarrhea, hematuria, and skin toxicity, not exceeding grade 2, as well as hypertension, not exceeding grade 3. NFTI-QOL scores remained stable or improved during treatment.
Conclusions: Axitinib therapy targeting VEGFR, PDGFR and c-KIT is feasible in this population and associated with volumetric and hearing responses in a subset of patients. However, convenience of oral administration should be balanced with respect to efficacy and safety of axitinib in comparison with other molecular-targeted therapies, including intravenous bevacizumab.
Keywords: NF2-related schwannomatosis; axitinib; phase 2 trial; vestibular schwannoma.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press, the Society for Neuro-Oncology and the European Association of Neuro-Oncology.
Figures

References
-
- Evans DG, Bowers NL, Tobi S, et al. Schwannomatosis: a genetic and epidemiological study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2018;89(11):1215–1219. - PubMed
-
- Plotkin SR, Messiaen L, Legius E, et al. ; International Consensus Group on Neurofibromatosis Diagnostic Criteria (I-NF-DC). Updated diagnostic criteria and nomenclature for neurofibromatosis type 2 and schwannomatosis: An international consensus recommendation. Genet Med. 2022;24(9):1967–1977. - PubMed
-
- Rugo HS, Herbst RS, Liu G, et al. Phase I trial of the oral antiangiogenesis agent AG-013736 in patients with advanced solid tumors: pharmacokinetic and clinical results. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(24):5474–5483. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Tortorici MA, Garrett M, et al. Clinical pharmacology of axitinib. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013;52(9):713–725. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
