RAF1 mutation expands the cardiac phenotypic spectrum of Noonan syndrome: A case report
- PMID: 40575432
- PMCID: PMC12186123
- DOI: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i6.106525
RAF1 mutation expands the cardiac phenotypic spectrum of Noonan syndrome: A case report
Abstract
Background: Noonan syndrome is a relatively common autosomal dominant genetic disorder characterized by cardiovascular defects owing to functional abnormalities in key genes such as RAF1. Mutations in RAF1 are typically associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). However, in this case, the patient exhibited atrial and ventricular septal defects (VSDs).
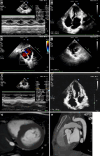
Case summary: This case report describes an 11-year-old boy diagnosed with Noonan syndrome, in whom genetic testing revealed a c.770C>T (p.Ser257 Leu) mutation in RAF1. The patient presented with intermittent chest discomfort and shortness of breath, symptoms that significantly worsened after physical activity. Clinical evaluation revealed marked growth retardation and multiple physical abnormalities. Electrocardiographic and echocardiographic assessments revealed VSDs, atrial septal defects, and left ventricular outflow tract obstruction. Following multidisciplinary consultation, the patient underwent cardiac surgical intervention, which led to clinical improvement; however, they subsequently developed a third-degree atrioventricular block, necessitating the implantation of a permanent pacemaker. During follow-up, echocardiographic findings demonstrated near-complete resolution of the shunt across the atrial and ventricular septa, significant improvement in left ventricular outflow tract obstruction, and notable reduction in ventricular septal thickness. A genetic mutation at the c.770C>T (p.Ser257 Leu) locus of RAF1 is typically associated with HCM and pulmonary hypertension. However, this patient's clinical phenotype manifested as HCM, atrial septal defect, and VSD, suggesting that this mutation may involve a different pathophysiological mechanism.
Conclusion: This case confirms the genotype-phenotype heterogeneity of Noonan syndrome and highlights the complex management requirements of RAF1 mutation-associated cardiac pathologies. Early surgical intervention can ameliorate structural defects, but it must be integrated with genetic counseling and lifelong monitoring to optimize patient outcomes.
Keywords: Atrial septal defect; Case report; Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; Noonan syndrome; RAF1 gene mutation; Ventricular septal defect.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

References
-
- Bell JM, Considine EM, McCallen LM, Chatfield KC. The Prevalence of Noonan Spectrum Disorders in Pediatric Patients with Pulmonary Valve Stenosis. J Pediatr. 2021;234:134–141.e5. - PubMed
-
- Gazzin A, Fornari F, Niceta M, Leoni C, Dentici ML, Carli D, Villar AM, Calcagni G, Banaudi E, Massuras S, Cardaropoli S, Airulo E, Daniele P, Monda E, Limongelli G, Riggi C, Zampino G, Digilio MC, De Luca A, Tartaglia M, Ferrero GB, Mussa A. Defining the variant-phenotype correlation in patients affected by Noonan syndrome with the RAF1:c.770C>T p.(Ser257Leu) variant. Eur J Hum Genet. 2024;32:964–971. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nakhaei-Rad S, Haghighi F, Bazgir F, Dahlmann J, Busley AV, Buchholzer M, Kleemann K, Schänzer A, Borchardt A, Hahn A, Kötter S, Schanze D, Anand R, Funk F, Kronenbitter AV, Scheller J, Piekorz RP, Reichert AS, Volleth M, Wolf MJ, Cirstea IC, Gelb BD, Tartaglia M, Schmitt JP, Krüger M, Kutschka I, Cyganek L, Zenker M, Kensah G, Ahmadian MR. Molecular and cellular evidence for the impact of a hypertrophic cardiomyopathy-associated RAF1 variant on the structure and function of contractile machinery in bioartificial cardiac tissues. Commun Biol. 2023;6:657. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li X, Yao R, Tan X, Li N, Ding Y, Li J, Chang G, Chen Y, Ma L, Wang J, Fu L, Wang X. Molecular and phenotypic spectrum of Noonan syndrome in Chinese patients. Clin Genet. 2019;96:290–299. - PubMed
-
- Pandit B, Sarkozy A, Pennacchio LA, Carta C, Oishi K, Martinelli S, Pogna EA, Schackwitz W, Ustaszewska A, Landstrom A, Bos JM, Ommen SR, Esposito G, Lepri F, Faul C, Mundel P, López Siguero JP, Tenconi R, Selicorni A, Rossi C, Mazzanti L, Torrente I, Marino B, Digilio MC, Zampino G, Ackerman MJ, Dallapiccola B, Tartaglia M, Gelb BD. Gain-of-function RAF1 mutations cause Noonan and LEOPARD syndromes with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Nat Genet. 2007;39:1007–1012. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

