Dual locking plate fixation, PRP-augmented autologous bone grafting, and bioactive core construction for femoral fracture nonunion: a retrospective study of 52 cases
- PMID: 40575570
- PMCID: PMC12198182
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1615628
Dual locking plate fixation, PRP-augmented autologous bone grafting, and bioactive core construction for femoral fracture nonunion: a retrospective study of 52 cases
Abstract
Background: Femoral nonunion remains a challenging orthopedic condition. This study evaluates a combined protocol integrating biomechanical stabilization (dual locking plate fixation) and maximal biological stimulation (PRP-augmented autologous bone grafting with bioactive core construction) to optimize bone healing.
Methods: A retrospective analysis included 52 femoral nonunion patients treated at a tertiary trauma center (2020-2024). Outcomes assessed radiographic union (9-month and final follow-up), clinical union time, thigh incision healing, pain scores (VAS), lower extremity function (LEFS), and complications.
Results: Cohort demographics: 35 males, 17 females; mean age 41.38 years, BMI 24.79 kg/m2. Nonunion subtypes: hypertrophic (36.5%, n = 19), atrophic (50%, n = 26), oligotrophic (13.5%, n = 7); locations: femoral shaft (63.5%, n = 33), supracondylar (36.5%, n = 19). All achieved union (mean follow-up: 19.01 months) with mean union time 6.56 ± 1.04 months. Postoperative outcomes: pain score 0.63 ± 0.97, LEFS 63.92 ± 5.92, incision healing 12.13 ± 1.36 days. The incidence rate of serious complications was 3.85% (2/52).
Conclusion: The protocol demonstrated efficacy and safety, achieving rapid union (6.56 months), robust functional recovery (LEFS 63.92), and a low incidence of serious complications (3.85%). Biomechanical-biological integration represents a viable strategy for femoral nonunion management.
Keywords: autologous iliac bone grafting; dual plate fixation; femoral fracture nonunion; fracture nonunion; platelet-rich plasma.
Copyright © 2025 Peng, Wang, Jie, Dai, Wang, Wu, Wu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
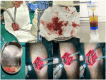
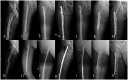
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pedicled medial femoral condyle corticoperiosteal flap for achieving union in patients with nonunion of the distal half of the femur (A short case series of three patients).BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 May 15;26(1):483. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08644-6. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40375222 Free PMC article.
-
[Augmenting locking plate with autologous bone graft for the treatment of nonunion of long bone fracture in the lower extremity with retaining of the original intramedullary nail].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2023 Dec 25;36(12):1191-5. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.2023.12.016. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2023. PMID: 38130231 Chinese.
-
Augmented Stability in Leaving Original Internal Fixation with Multidimensional Cross Locking Plate through Mini-Open Femoral Anterior Approach for Aseptic Femoral Shaft Nonunion: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Orthop Surg. 2023 Jan;15(1):169-178. doi: 10.1111/os.13581. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Orthop Surg. 2023. PMID: 36411511 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for treating fractures of the distal femur in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Oct 5;10(10):CD010606. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010606.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36197809 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of Bone-Healing by Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound: A Systematic Review.JBJS Rev. 2016 Mar 29;4(3):e6. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.O.00027. JBJS Rev. 2016. PMID: 27500435
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

