Diabetic kidney disease in rural Australia: prevention, management, treatment and way forward
- PMID: 40575571
- PMCID: PMC12198140
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1561566
Diabetic kidney disease in rural Australia: prevention, management, treatment and way forward
Abstract
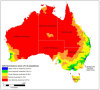
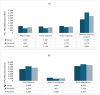
Diabetic kidney disease is a significant microvascular complication associated with chronic diabetes, contributing substantially to the overall health burden of the disease. This perspective focusses on evaluating the most recent advancements in screening techniques, prevention, and treatment strategies along with new advances in the field. A comprehensive literature search was conducted across PubMed, Scopus and Google Scholar databases to identify and synthesize recent evidence. In Australia, chronic kidney disease (CKD) was responsible for approximately two million hospital admissions, accounting for 18% of all hospitalizations in 2021-22. In remote areas, 17,100 CKD-related hospitalizations were reported during this period, with residents being three times more likely to be hospitalized for CKD compared to those living in major cities. Among First Nations people, the burden was 7.8 times higher than that of non-Indigenous populations. Advocacy for policy changes to address healthcare disparities in rural and remote Australia is crucial.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease (CKD); diabetic kidney disease (DKD); management; prevention; rural Australia; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2025 Ross, Mondal, Anyasodor, Mahmood, Astawesegn, Huda, Thapa, Aychiluhm, Giri, Rahman, Shiddiky, Moni and Ahmed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early referral strategies for management of people with markers of renal disease: a systematic review of the evidence of clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and economic analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2010 Apr;14(21):1-184. doi: 10.3310/hta14210. Health Technol Assess. 2010. PMID: 20441712
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers for adults with early (stage 1 to 3) non-diabetic chronic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Oct 5;(10):CD007751. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007751.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 19;7:CD007751. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007751.pub3. PMID: 21975774 Updated.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers for adults with early (stage 1 to 3) non-diabetic chronic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 19;7(7):CD007751. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007751.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37466151 Free PMC article.
-
Multidisciplinary management of diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Jul;14(7):169-207. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-003011. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532796
References
-
- Pharmaceutical Benifits Scheme (PBS), Department of Health and Aged care . Available online at: https://www.pbs.gov.au/info/about-the-pbs (Accessed May 13, 2025).
-
- Rural and Remote Health . Available online at: https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/rural-remote-australians/rural-and-remot... (Accessed May 13, 2025).
-
- Australia's Health 2022: in Brief . Available online at: https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/australias-health/australias-health-2022... (Accessed May 13, 2025).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

