COVID-19 management in patients with comorbid conditions
- PMID: 40575645
- PMCID: PMC12188852
- DOI: 10.5501/wjv.v14.i2.102674
COVID-19 management in patients with comorbid conditions
Abstract
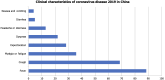
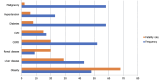
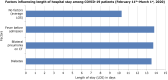
The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) causes serious respiratory illness and related disorders. Vulnerable populations, including those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, heart disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, obesity, and the elderly, face an increased risk of severe complications. As the pandemic evolves, various diagnostic techniques are available to detect severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (SARS-CoV-2), including clinical presentation, rapid antigen/antibody testing, molecular testing, supplemental laboratory analysis, and imaging. Based on peer-reviewed data, treatment options include convalescent plasma transfusion, corticosteroids, antivirals, and immunomodulatory medications. Convalescent plasma therapy, historically used in outbreaks like Middle East respiratory syndrome, Ebola, and SARS, is suggested by the World Health Organization for critically ill COVID-19 patients when vaccines or antiviral drugs are unavailable. Neutralizing antibodies in convalescent plasma help control viral load and improve patient outcomes, especially when administered early, though effectiveness varies. The United States Food and Drug Administration has authorized its emergency use for severe COVID-19 cases, but potential risks such as transfusion reactions and transfusion-related acute lung injury require further investigation to establish definitive efficacy. Antiviral agents like Remdesivir, an adenosine nucleotide analog, inhibit viral RNA polymerase and have shown efficacy in reducing COVID-19 severity, leading to its emergency use authorization for hospitalized patients. Other antivirals like ritonavir, lopinavir, and umifenovir disrupt viral replication and entry, but their effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 remains under investigation. Dexamethasone, a corticosteroid, has been used in critically ill COVID-19 patients to reduce inflammation and prevent respiratory failure, as shown in the RECOVERY trial. Other immunosuppressants like ruxolitinib, baricitinib, and colchicine help modulate the immune response, reducing cytokine storms and inflammation-related complications. However, corticosteroids carry risks such as hyperglycemia, immunosuppression, and delayed viral clearance, requiring careful administration. Systematic reviews of clinical studies revealed that hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin did not decrease viral load nor reduce the severity of symptoms, but increased mortality among acutely hospitalized patients. There was no improvement in patients' clinical conditions after 15 days compared to standard treatment. The United States Food and Drug Administration has revoked the authorization for the use of hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 patients due to the null benefit-risk balance. Monoclonal antibodies like itolizumab, gimsilumab, sarilumab, and tocilizumab are being studied for their ability to reduce the severe inflammatory response in COVID-19 patients, particularly cytokine release syndrome and acute respiratory distress syndrome. These antibodies target specific immune pathways to decrease pro-inflammatory cytokines, with some showing promising results in clinical trials, though their use remains under investigation. The Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/Cas13 family of enzymes, sequenced from many COVID-19-positive patients, can potentially inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication, cleave the RNA genome, and aid in the amplification of the genome assay. Cas13 can also target emerging pathogens via an adeno-associated virus vector when delivered to the infected lungs. In addition to pharmacological agents, vaccines effectively prevent symptomatic infection, reduce hospitalizations, minimize mortality rates, and ultimately reduce the severity of the disease. This paper aims to explore the management of patients with underlying conditions who present with COVID-19 to lessen the burden on healthcare systems.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chemotherapy; Comorbidity; Diabetes; Heart disease; Therapeutic management; Vaccine.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Conditions contributing to deaths involving coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), by age group and state, United States. [cited 26 December 2024]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/health_policy/covid19-comorbidity-expanded... .
-
- Ozturk S, Turgutalp K, Arici M, Odabas AR, Altiparmak MR, Aydin Z, Cebeci E, Basturk T, Soypacaci Z, Sahin G, Elif Ozler T, Kara E, Dheir H, Eren N, Suleymanlar G, Islam M, Ogutmen MB, Sengul E, Ayar Y, Dolarslan ME, Bakirdogen S, Safak S, Gungor O, Sahin I, Mentese IB, Merhametsiz O, Oguz EG, Genek DG, Alpay N, Aktas N, Duranay M, Alagoz S, Colak H, Adibelli Z, Pembegul I, Hur E, Azak A, Taymez DG, Tatar E, Kazancioglu R, Oruc A, Yuksel E, Onan E, Turkmen K, Hasbal NB, Gurel A, Yelken B, Sahutoglu T, Gok M, Seyahi N, Sevinc M, Ozkurt S, Sipahi S, Bek SG, Bora F, Demirelli B, Oto OA, Altunoren O, Tuglular SZ, Demir ME, Ayli MD, Huddam B, Tanrisev M, Bozaci I, Gursu M, Bakar B, Tokgoz B, Tonbul HZ, Yildiz A, Sezer S, Ates K. Mortality analysis of COVID-19 infection in chronic kidney disease, haemodialysis and renal transplant patients compared with patients without kidney disease: a nationwide analysis from Turkey. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020;35:2083–2095. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. People with certain medical conditions and COVID-19 risk factors. [cited 7 March 2025]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/covid/risk-factors/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.go... .
-
- Marron RM, Zheng M, Fernandez Romero G, Zhao H, Patel R, Leopold I, Thomas A, Standiford T, Kumaran M, Patlakh N, Stewart J, Criner GJ and the Temple University COVID-19 Research Group. Impact of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Emphysema on Outcomes of Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia. Chronic Obstr Pulm Dis. 2021;8:255–268. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

