Biophysical basis of tight junction barrier modulation by a pan-claudin-binding molecule
- PMID: 40575703
- PMCID: PMC12198772
- DOI: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgaf189
Biophysical basis of tight junction barrier modulation by a pan-claudin-binding molecule
Abstract
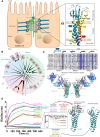
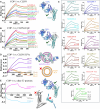
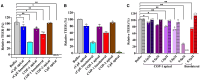
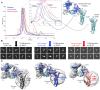
Claudins are a 27-member family of membrane proteins that form and fortify specialized cell contacts in endothelium and epithelium called tight junctions. Tight junctions restrict paracellular transport through tissues by forming molecular barriers between cells. Claudin-binding molecules thus hold promise for modulating tight junction permeability to deliver drugs or as therapeutics to treat tight junction-linked disease. The development of claudin-binding molecules, however, is hindered by their physicochemical intractability and small targetable surfaces. Here, we determine that a synthetic antibody fragment (sFab) that we developed binds with nanomolar affinity directly to 10 claudin subtypes and other distantly related claudin family members but not to other tight junction-localized membrane proteins. It does so by targeting the extracellular surfaces of claudins, which we verify by applying this sFab to a model intestinal epithelium and observe that it opens paracellular barriers comparable to a known, but application limited, tight junction modulating protein. This pan-claudin-binding molecule holds potential for both basic and translational applications as it is a probe of claudin and tight junction structure in vitro and in vivo and a tool to modulate the permeability of tight junctions broadly across tissue barriers.
Keywords: claudin; drug delivery; membrane proteins; synthetic antibody; tight junctions.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of National Academy of Sciences.
Figures

Update of
-
Biophysical Basis of Paracellular Barrier Modulation by a Pan-Claudin-Binding Molecule.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 11:2024.11.10.622873. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.10.622873. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: PNAS Nexus. 2025 Jun 06;4(6):pgaf189. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgaf189. PMID: 39605593 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Biophysical Basis of Paracellular Barrier Modulation by a Pan-Claudin-Binding Molecule.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 11:2024.11.10.622873. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.10.622873. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: PNAS Nexus. 2025 Jun 06;4(6):pgaf189. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgaf189. PMID: 39605593 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A multi-pore model of the blood-brain barrier tight junction strands recapitulates the permeability features of wild-type and mutant claudin-5.Protein Sci. 2025 Sep;34(9):e70271. doi: 10.1002/pro.70271. Protein Sci. 2025. PMID: 40862374 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysics of claudin proteins in tight junction architecture: Three decades of progress.Biophys J. 2024 Aug 20;123(16):2363-2378. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.06.010. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Biophys J. 2024. PMID: 38859584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

