Systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance in MRSE Isolated from Iranian patients
- PMID: 40575738
- PMCID: PMC12194433
- DOI: 10.22088/cjim.16.2.225
Systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance in MRSE Isolated from Iranian patients
Abstract
Background: Biofilms are organized communities of microorganisms encased in a self-produced matrix that adheres to surfaces and can have both beneficial and detrimental effects in various environments. These biofilms have been linked to severe infections in humans. We investigated the association between antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) isolates.
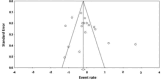
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted through data medical data bases using a combination of mesh terms. The data were analyzed using STATA meta-analysis software, and a random effects model was employed to determine the pooled prevalence with a 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results: Our findings revealed that the prevalence of MRSA was 61.75% (95% CI: 35.6-99.1). The cumulative rate of biofilm formation in MRSE strains was reported to be 83.4% (95% CI: 47.8-99.4). Among the biofilm-related genes, the SdrG gene exhibited the highest frequency (98%), followed by the atlG gene with a frequency of 84%.
Conclusion: Out of the seven, three documented a positive association. Given the propensity of MRSE strains to form biofilms, it is crucial to implement preventive measures against infections caused by these strains.
Keywords: Biofilm formation; Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis.
© The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sah S, Bordoloi P, Vijaya D, et al. Simple and economical method for identification and speciation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and other coagulase negative Staphylococci and its validation by molecular methods. J Microbiol Methods. 2018;149:106–19. - PubMed
-
- Lee SM, Keum HL, Sul WJ. Bacterial crosstalk via antimicrobial peptides on the human skin: Therapeutics from a sustainable perspective. J Microbiol. 2023;61:1–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources