Transport and thiazide-inhibition mechanisms of the Na-Cl cotransporter: a structural perspective
- PMID: 40575829
- PMCID: PMC12337910
- DOI: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000001099
Transport and thiazide-inhibition mechanisms of the Na-Cl cotransporter: a structural perspective
Abstract
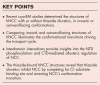
Purpose of review: The structures of the human sodium-chloride cotransporter (hNCC) and its complex with thiazide diuretics have been determined recently. This review summarizes key structural insights into NCC's transport and inhibition mechanisms.
Recent findings: Recent studies revealed the structures of hNCC and its complex with thiazide diuretics, in inward-facing and outward-facing conformations, respectively. The structures of hNCC in two major conformational states provided important insights into the transport and regulatory mechanisms. Thiazide-bound hNCC structures illuminated the molecular mechanisms of thiazide-mediated NCC inhibition and explained the structure-activity relationship of thiazide diuretics.
Summary: Structures of hNCC provide mechanistic insights into molecular mechanisms of loss-of-function NCC variants that cause Gitelman syndrome. The thiazide-bound hNCC structures provide a blueprint for further optimizing thiazide diuretics to reduce side effects. The novel interdomain interaction-mediated hNCC regulatory mechanisms revealed by structural studies lay the foundation for developing next-generation NCC modulators and NCC-rescuing therapeutics for treating NCC dysfunction.
Keywords: cotransporter; cryo-EM; protein structures; sodium-chloride cotransporter; thiazide diuretics; transporter.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanisms of thiazide-like diuretics-mediated inhibition of the human Na-Cl cotransporter.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 20;16(1):7740. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62714-w. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40830368 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and thiazide inhibition mechanism of the human Na-Cl cotransporter.Nature. 2023 Feb;614(7949):788-793. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05718-0. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Nature. 2023. PMID: 36792826 Free PMC article.
-
Blood pressure-lowering efficacy of monotherapy with thiazide diuretics for primary hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 May 29;2014(5):CD003824. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003824.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24869750 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insights from dysregulation of the thiazide-sensitive WNK/SPAK/NCC pathway in the kidney: Gordon syndrome and thiazide-induced hyponatraemia.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2013 Dec;40(12):876-84. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12115. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23683032 Review.
-
Thiazide diuretics alone or combined with potassium-sparing diuretics to treat hypertension: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Hypertens. 2023 Jul 1;41(7):1108-1116. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003436. Epub 2023 Apr 3. J Hypertens. 2023. PMID: 37016911 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu A, Wolley M, Stowasser M. The interplay of renal potassium and sodium handling in blood pressure regulation: critical role of the WNK-SPAK-NCC pathway. J Hum Hypertens 2019; 33:508–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

