Lobaric Acid Exhibits Anticancer Potential by Modulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in MCF-7 Cells
- PMID: 40576246
- PMCID: PMC12203569
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.70142
Lobaric Acid Exhibits Anticancer Potential by Modulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in MCF-7 Cells
Abstract
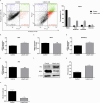
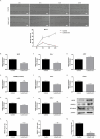
Lichen secondary metabolites with many remarkable biological activities are used in cancer treatments due to their low side effects and high anticancer potential. In particular, these metabolites constitute an interesting research area in cancer treatments due to their potential to induce apoptosis and suppress metastasis by inhibiting cancer-related signaling pathways. The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway plays a role in important biological processes such as oncogenesis, cell cycle regulation, cell proliferation, metastasis, differentiation, apoptosis, and drug resistance. Therefore, inhibition of this pathway is a potential target in cancer therapies. There is no detailed study explaining the potential anticancer molecular mechanism of the lichen secondary metabolite lobaric acid (LA) on breast cancer. Here, it is aimed to investigate the effect of LA on viability, apoptosis, and migration in MCF-7 cells and to elucidate the relationship between the potential anticancer effect and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The dose- and time-dependent viability of LA-treated MCF-7 cells was evaluated by XTT assay, and the IC50 value was determined as 44.21 μg/mL at 48 h. LA increased the apoptotic cell population, as shown by flow cytometry analysis, qPCR, and Western blot results. LA inhibited β-catenin by inducing GSK3-β protein expression, thereby suppressing Wnt/β-catenin target genes. LA might be a natural active compound candidate for breast cancer treatment.
Keywords: Wnt/β‐catenin pathway; apoptosis; breast cancer; cytotoxicity; expression.
© 2025 The Author(s). Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of dendrosomal nanocurcumin on Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via PIWIL2 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.Med Oncol. 2025 Jul 28;42(9):381. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02960-6. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40719975
-
A New Treatment Strategy for Lung Cancer With HDAC and Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Inhibitors.IUBMB Life. 2025 Jul;77(7):e70037. doi: 10.1002/iub.70037. IUBMB Life. 2025. PMID: 40650414 Free PMC article.
-
Novel indole Schiff base β-diiminato compound as an anti-cancer agent against triple-negative breast cancer: In vitro anticancer activity evaluation and in vivo acute toxicity study.Bioorg Chem. 2024 Nov;152:107730. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107730. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Bioorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 39216194
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Ozgencli I., Budak H., Ciftci M., and Anar M., “Lichen Acids May be Used as A Potential Drug for Cancer Therapy; by Inhibiting Mitochondrial Thioredoxin Reductase Purified From Rat Lung,” Anti‐Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry 18, no. 11 (2019): 1599–1605, 10.2174/1871520618666180525095520. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

